
Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone, named after its importance in the estrous cycle of humans. The estrous cycle refers to the recurring physiologic changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in females. Estrous cycles start after puberty, and they are interrupted by anestrous phases or pregnancies. Estrogens are also used as part of some oral contraceptives, also referred to as the birth-control pills. Birth control contraceptives are taken to inhibit female fertility, ever since the 1960’s. Estrogen is often combined with progestin, another female hormone, to prevent ovulation, or the release of eggs from the ovaries.
How does birth control medication work?
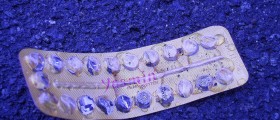
Oral contraceptives are usually delivered in packages containing 21, 28, or 91 tablets. One tablet is taken by mouth once a day, every day of a regular cycle. Estrogen and progestin in the tablets can prevent the ovulation and change the lining of the uterus to prevent the pregnancy from developing. These hormones in the form of tablets are also responsible for changes in the mucus in the uterus. Hormones are able to thicken the mucus and therefore, prevent male reproductive cells, from entering.
As a positive side effect, oral contraceptives can treat acne problems in certain patients and even relieve the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. Sometimes, oral contraceptives are prescribed in treatment of mild hormonal deficiencies, irregular menstruation, and endometriosis.
Use of the pill for emergency contraception
Sometimes, standard birth control pills can be taken to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse. For example, a woman may want to take emergency contraception after an unprotected sex, if condom breaks, if a diaphragm slips out of place during the intercourse, or after a sexual attack. This pill, also known as the “morning after pill” is taken within 72 hours of unprotected sex, to effectively reduce the possibility of pregnancy. These pills actually contain high doses of the same hormones, estrogen and progestin, that are normally found in birth control pills. Emergency contraceptive pills, which are available by prescription only, are taken in two doses 12 hours apart. The first dose is taken within the first 72 hours after the intercourse, reducing the chance of pregnancy by 75%.
Side effects of emergency contraception
Oral contraceptives can sometimes cause side effects. The most common complaint is nausea accompanied with vomiting, diarrhea, constipation or stomach cramps. Therefore, doctors advise to take oral contraceptives with food or milk to avoid gastrointestinal problems. Other side effects include gingivitis, changes in the appetite, weight gain or weight loss, brown or black skin patches, acne and hair growth.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...