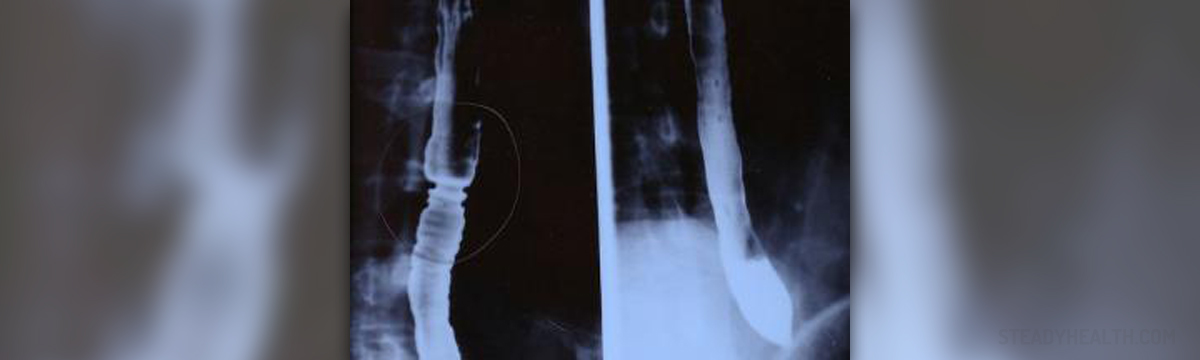
The esophagus is a muscular organ and a part of the gastrointestinal tract. It is in charge of the transfer of food, fluids and saliva from the pharynx to the stomach. In adults the esophagus is approximately 10 inches long. It is located in the posterior mediastinum, between the trachea and the spine. This inner surface of the esophagus contains a lot of glands that keep the inside of the organ moist and assist in the process of swallowing. During the act of swallowing the food passes from the mouth, reaches the pharynx and enters the esophagus and is then transferred into the stomach via peristalsis.
What Is Function of the Esophagus?
The organ comprises of three parts - cervical, thoracic and abdominal part. They all contract in a specific manner during the process of swallowing.
The organ represents a vital part of the gastrointestinal tract and is essential for proper transport of food, fluids and saliva from the oral cavity into the stomach. The esophagus can perform its role thanks to a layer of muscles that make the wall of the organ. Adequate contraction of the esophageal muscles allows the food to pass down the organ and into the stomach. Once the food from the mouth reaches the esophagus its muscles start to contract and push the food to the lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Once the process begins the upper sphincter muscle closes and prevents regurgitation of the food into the mouth. And finally, once the food enters the stomach the lower sphincter muscle of the esophagus closes and does not allow food to return back from the stomach.
Abnormalities of Esophageal Function
If there are no structural or functional abnormalities the esophagus performs its role quite efficiently. However, in some cases the organ can be damaged and the process of swallowing may become difficult. The damage to the organ is seen in people who consume plenty of alcohol or eat spicy food or drink carbonated drinks on regular bases. Furthermore, the inner surface of the organ is affected in some medical conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease when the damage occurs due to regurgitation of the stomach acid. Achalasia is an esophageal motility disorder that leads to serious difficulties with swallowing. Esophageal diverticulitis affects different parts of the esophagus. There are three types of diverticula - Zenker's diverticulum, traction diverticulum and ephiphrenic diverticulum. All of them may cause problems during the act of swallowing. And finally, improper function of the esophagus always occurs in case of advanced esophageal cancer.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...