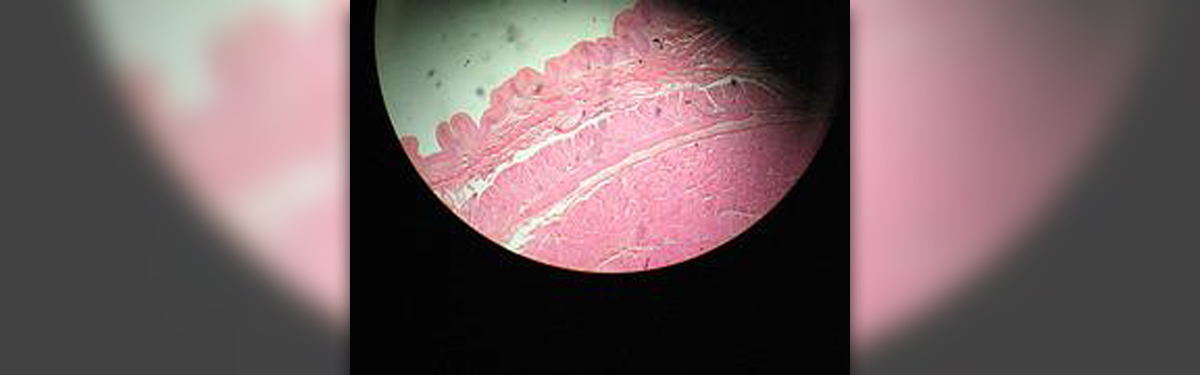
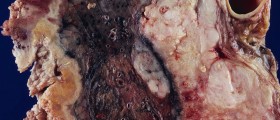
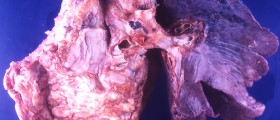
A patient who experiences the prevalence of Barrett metaplasia in adenocarcinoma of the esophagus can suspect of cancer of the esophagus as that Barrett esophagus is considered to be a precancerous condition. Endoscopic surveillance is essential for patients who are diagnosed with Barrett metaplasia because that kind of surveillance can lead to identification of the cancer in its early stages. If the cancer is diagnosed early the chances of survival are a lot higher. This fact is especially vital for patients suffering from esophageal cancer because the survival rate is extremely low in these patients. In a majority of situations asymptomatic tumors are discovered by mere chance.
Esophageal Tumor Obstruction
In a situation where the patient is experiencing a complete esophageal obstruction but without clinical evidence of systemic metastasis, the most often used way of treatment is a surgical procedure. The procedure consists of the removal of the tumor along with the mobilization of the stomach in order for the esophagus to be replaced.
An average age of patients suffering from cancer of the esophagus in the United States is 67 years. A retrospective review was done on a single team of specialists who operated on 505 consecutive patients during a period of 17 years. The data shows no difference between older patients and those of younger age when preoperative mortality, median survival and the palliative benefit of esophagectomy on dysphagia are considered. This review proved that age should not be the only factor when it needs to be determined whether a patient should undergo a surgical procedure or not.
How is Esophageal Cancer Managed
Throughout the history, the prognosis for esophageal cancer was never good. One of the main and most significant reasons why that is so, is the fact that the patients were diagnosed with the disease when it was already in one of the advanced stages. When cancer has progressed surgery is an option only is some rare situations. Another problem that occurs is the location of the esophagus which makes high-dose definitive radiation therapy almost impossible. Every radiation portal encompassing the esophagus will also include some of the other structures that are close like blood vessels, major airways and even the heart and lungs. This radiation is supposed to be an alternative treatment for surgical resection. Modern radiation therapy causes less side effects but the doses of toxicity are the same because the dose of radiation does not change. A historical review of the outcomes after treatments for cancer of the esophagus showed was published in the year of 1980. According to that review, the overall survival rate for a period of 5 years after surgical resection was only 4%. On the other hand, survival rate in the same period after radiation therapy was 6%. 30% was the rate of surgical mortality.
However, over the years the rate of survival has changed. The results after surgical procedures as treatments for esophageal cancer have increased drastically. The survival rate between 13 months and 2 years in patients who underwent one or multiple surgical procedures in order to treat esophageal cancer are now between 35 and 42%. A 5-year survival rate is no longer 4% but between 15 and 24%. Even though the numbers are a lot better than they were 30 years ago, they are still not considered to be a success. One of the main reasons why the numbers have improved is because of better clinical staging.
The resection of the primary tumor and the draining of lymph nodes are the main goals for oncologic surgery. Radiation therapy has showed success and any actual effect on patients who were diagnosed with early stages of esophageal cancer and only in these situations radiation therapy affects the 5-year survival rate. If the patient is suffering from cancer of the esophagus that has progressed, the doctors use radiation therapy as a single-modality approach with curative intent. It is considered to be a palliative intervention in those patients whose underlying medical comorbidities rule put surgical procedure or aggressive multimodality treatment.
Multimodality treatment options were not available until a couple of years ago. However, the results when these combinations and sequences were used were not always promising.
Chemotherapy is another option for patients diagnosed with cancer of the esophagus. Chemotherapy can be administrated either before the operation or after it. Some patients require chemotherapy both before and after the operation. Several studies were done on the increase of 5-year survival in patients who received chemotherapy before the surgery but the results were mixed.
Those patients who are diagnosed with metastatic disease undergo a treatment with palliative intent. The first goal of palliation is relief of dysphagia and esophageal obstruction. More than one way in which this can be achieved exists. Some of the most often used ones are palliative radiation, endoscopic dilation, endoscopic laser therapy and endoscopic stenting. However, this therapy does not have a great impact on the survival rate.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...