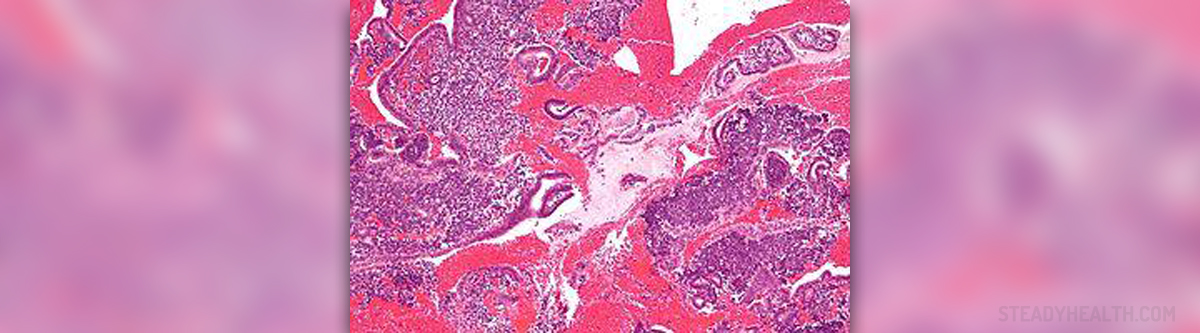
Endometrial hyperplasia is the term that refers to abnormal thickening of the endometrium due to excessive growth of glandular tissue. In the majority of cases endometrial hyperplasia is not a serious medical condition and is easily treated by a well experienced gynecologist.
Endometrial hyperplasia frequently affects menopausal women as well as those who are about to enter menopause. This drives to conclusion that the condition is somehow connected with hormonal changes. The condition is not malignant per se, but sometimes carries risk of further development to endometrial cancer. This is the reason why all women suffering from endometrial hyperplasia must be closely monitored, particularly those with specific types of the condition. During a Pelvic Exam
Women may come for regular check-up or turn to their gynecologist because they have some gynecological problems. In both cases, doctors first take a medical history and then perform a pelvic exam.
It may be necessary to rule out pregnancy and infections. Also during a pelvic exam, gynecologists perform a Pap test (the efficient means of confirming or ruling out cervical cancer).
Since it is simply not possible to have insight in the cavity of the uterus during a pelvic exam, patients additionally undergo ultrasound. Ultrasound successfully confirms thickening of the endometrium. In order to rule out endometrial cancer, doctors perform biopsy of the endometrium and send samples for pathohistological examination. If there is a need, a woman may also undergo hysteroscopy.
After pathohistological examination, endometrial hyperplasia is confirmed. It is also possible to determine the type of hyperplasia. Endometrial Hyperplasia Treatment Options
Some women are only monitored. Others can be treated conservatively or surgically. Medicamentous treatment consists of prescription-strength progesterone/progestin therapy. These drugs are taken for three months. The results are satisfactory in case of mild disease. Some women may also benefit from compounded bioidentical progesterone.
In case there is atypia associated with endometrial hyperplasia women may be prescribed Megace. This is a very potent hormonal agent and is recommended for women who refuse to undergo surgery because they plan to get pregnant in the future. During this treatment, regular check-ups are mandatory.
Under certain circumstances, surgical removal of the uterus may be inevitable and the only way to preserve a woman's health. Unfortunately, once the uterus is surgically removed, a woman cannot conceive again.
Finally, some women are left with no option but to undergo surgical removal because in them endometrial hyperplasia is rather severe. This can be quite devastating because it is hard to face the fact that a woman's ability to become a mother is going to be lost forever.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...