
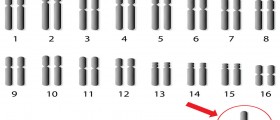
Down syndrome is a variant of a condition called trisomy 21, due to the fact that it is caused by an extra chromosome being present on the 21st chromosome. There are several types of Down syndrome and these can vary in severity and characteristics. However, all of these types affect the mental or physical health of an individual negatively.
Signs of Down Syndrome
Again, the symptoms may vary, depending on the severity of this condition. Yet, most commonly, people with Down syndrome have heads which are smaller than normal, being round and flat on the back. Also the inner corners of the eyes may be rounded and the face may be flat as well.
As for other physical signs of this syndrome, reduced muscle tone at birth, additional skin at the neck or the nape, flat nose, gaps between joints of the bones and the skull, a single crease on the palms, small ears and mouth, eyes slanting upwards, short hands and legs and white spots on the colored parts of the eyes, all are distinctive features of people with Down syndrome.
Due to these factors, a vast majority of people with this condition never manage to reach normal body build or adult height. Other, mental, complications which might go hand-in-hand with Down syndrome are impulsiveness, lack of proper judgment, concentration difficulties and learning disabilities. As children with Down syndrome get older, they usually become frustrated and angry due to their limitations in comparison to other, healthy children.
Additional Complications
Some severe occurrences of Down syndrome may appear along with other illnesses and defects. Some of these are dementia and Alzheimer's, heart conditions, visual and hearing impairments, gastrointestinal dysfunctions, hip problems, chronic constipation, sleep apnea, dental irregularities and thyroid abnormalities.
Diagnosis and Additional Information
Diagnosis mostly relies on the physical symptoms, even though stethoscope and blood tests are used to confirm the doubts. Additionally, ECG and X-ray scans can be used for these purposes. Moreover, children and people with Down syndrome need to undergo regular medical checkups often, preventing complications and maintaining their proper health.
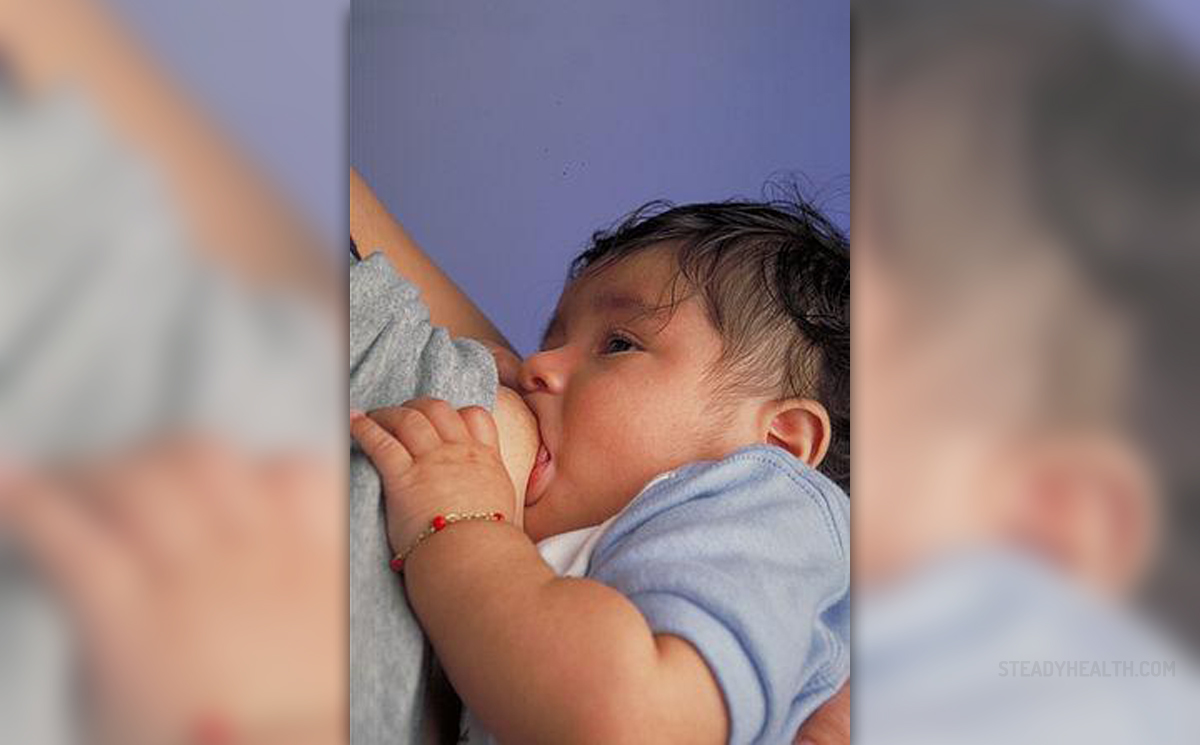
Breastfeeding and Down Syndrome
Babies with Down syndrome may find it hard to suck the milk out properly during breastfeeding. In these situations, you might need to force the milk out by yourself and hold the nipple inside the baby's mouth so that it does not fall out. Additionally, make sure you support the baby well, holding his/her head, jaw and body in an adequate position. Alternatively, you can use a pillow or a carrier in order to secure your baby, freeing one of your hands this way, using it to hold the baby.
Even though breastfeeding may be complicated, you need to provide it for your baby since Down syndrome makes babies prone to infections and health problems.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...