
Down syndrome is a medical condition also known as Trisomy 21. Children born with this condition have an extra chromosome, an excessive amount of genetic material, which confuses the body and causes various delays in child’s development. This is a very rare condition, but almost all of us have sometimes seen a child with Down syndrome. Actually, this condition affects about one in every eight hundred babies. Each of the little patients is affected in its own way, and the features and medical symptoms usually widely vary from one to another patient. Some of the children affected with Down syndrome may live completely normal lives, while the others need extra care and rigorous medical attention.
Causes of Down syndrome
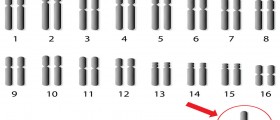
Down syndrome is a hereditary disorder. This means that health problems occur because of the problems in the child’s genes. Normally, each baby carries genetic information received from both mother and father. This information includes a set of 46 chromosomes, half of which are coming from mother, while the other half comes from father. In Down syndrome, a child has 47 instead of the 46 chromosomes, and this additional genetic information causes a wide array of symptoms.Symptoms of Down syndromeChildren with Down syndrome may have different manifestations of this disease but, normally, they share some characteristic physical features. A child with Down syndrome usually has a flat facial profile, very small ears, an upward slant to the eyes, and a protruding tongue. Their muscle tone is very low and they typically learn to sit up, to crawl and to walk much later than the normal kids do. These children grow at the slower rate, and in most of the cases they are not as bright as healthy children. However, children with Down syndrome may develop some other skills than learning and be brilliant on many different fields.
Unfortunately, in most of the cases, children with Down syndrome have a congenital heart defect. They are also at increased risk of developing pulmonary hypertension, visual and hearing problems.
Prevention of Down syndromeDown syndrome can normally be detected during the pregnancy, before the child is born. This makes it possible to prevent it. Women older than the age of 35 are at an increased risk of having a baby with Down syndrome. If a woman is pregnant at the age 30, her chances to deliver a baby with Down syndrome is only 1 in 900. However, when the women have 40 years while she is pregnant, her chances rise to 1 in 100.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...