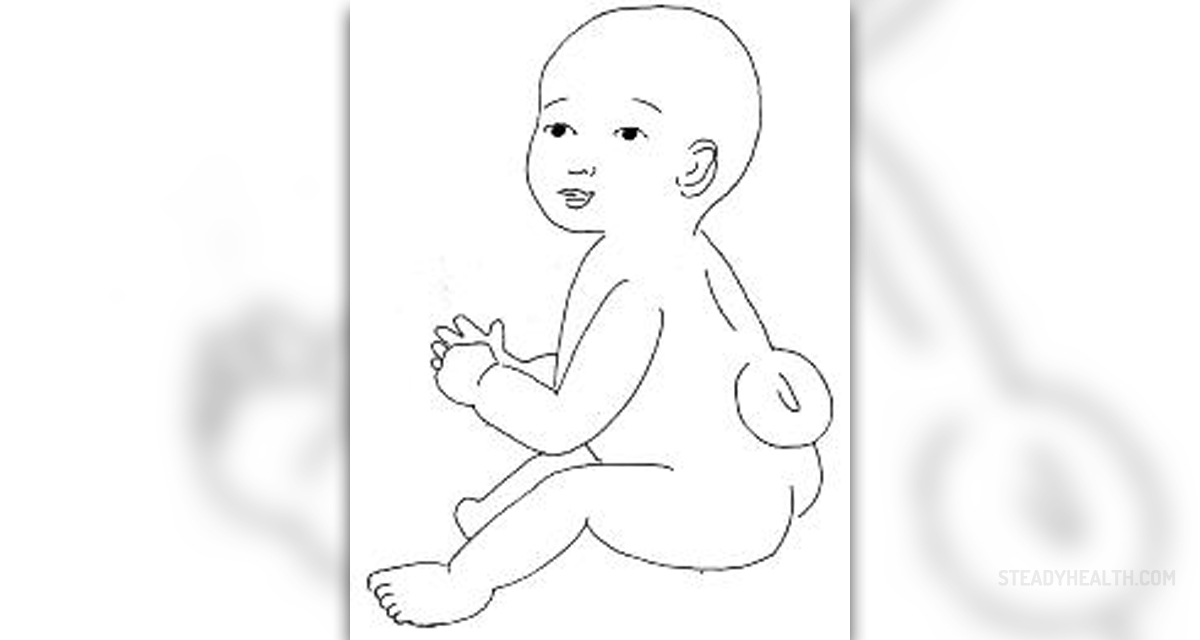
Neural tube defects are medical conditions which occur inevery 1000th live birth in the United States. Medically speaking, aneural tube defect can be characterized as an opening in the brain or thespinal cord and it always occurs in the early stages of the fetal development. Thesecond week of pregnancy is referred to as gastrulation and it is the exactperiod when the neural tube gets formed when the specialized cells fuse on thedorsal side of the fetus. In case this tube does not get closed properly, it is asituation in which the harmful neural tube defects start taking place. VitaminB12 and folic acid are very important elements when it comes to reducing therisk of different types of neural tube defects. Folate is essential in the synthesisof the DNA and RNA and the production and maintenance of all new cells inthe human body. Another important role of folate is transfer ofa certain carbon group so that it can be methylated and also proper synthesisof the nucleic acid. Vitamin B12 is one of the most important receptors in thebiopathway of the folic acid. The exact causes of neural tube defects arelargely unknown and cannot be pin pointed, but there are still certain oneswhich may be associated with this type of medical condition. They includematernal cigarette smoking, maternal exposure to second hand smoke, radiation,hyperthermia in early development, exposure to arsenic, mycotoxins in contaminated cornmeal, maternal obesity, maternal diabetes and different sorts of folateantimetabolites.
Classification of Neural Tube Defects
All neural tube defects can be divided into two groups – closed neural tube defects and open neural tube defects. Open neural tube defectsare much more common and they occur when the spinal cord or the brain getexposed at birth due to some physical defect in the back bones or the skull.The most frequent types of open neural tube defects include spina bifida,schizencephaly, iniencephaly, hydranencephally, encephaloceles and anencephaly.Closed types of neural tube defects are relatively rare and they are usually associated with certain spinal defects which are covered by skin. The mostcommon types of closed neural tube effects include the tethered cord,lipomeningocele and lipomyelomeningocele. Spina bifida is a type ofopen neural tube defects and it can be divided into two subtypes known as spina bifida occulta and spina bifida cystica. Spina bifida occultais a medical condition that affects the meninges which donot herniate through the opening in the spinal canal. In most cases, thismedical condition is not considered to be harmful as it does not involve thespinal nerves or the spinal cord. Spina bifida cystic is different as itinvolves the presence of myelomeningocele which is characterized by herniation of the meningesand the spinal cord or meningocele which is less severe and it involves onlyherniation of the meninges. Iniencephally is one of the rarest types ofopen neural tube defects and it is triggered by extreme bending of thehead to the spine. In most cases, the neck is absent, the skin of the faceconnected to the chest and the scalp connected to the upper back. The infantcannot survive for more than a few hours. Hydranencephaly is another type ofopen neural tube defect in which cerebral hemispheres are filled withsacs of cerebrospinal fluid. Anencephaly is one of the most severe types ofopen neural tube defects and it is characterized by a complete absence of the major part of thebrain and the skull. The infant is commonly blind, unconscious and deaf.
Diagnosis
There are certain tests which need to be conducted in orderto confirm the presence of a neural tube defect. Such tests include themeasurement of maternal serum alpha fetoprotein and ultrasound examination.Additional tests which may also be required in some cases include amnioticfluid acetylcholinesterase and amniotic fluid alpha fetoprotein tests.
Prevention
Fortunately enough, there are certain measures which can betaken in order to prevent neural tube defects from occurring in the firstplace. Any pregnant woman or a woman trying to conceive needs tobe well aware of the fact that folic acid supplements may prevent more thanhalf the cases of neural tube defects. They need to be taken one month beforethe actual conception and all the way until the end of the first three monthsof pregnancy. The recommended daily dose is 400 micrograms but pregnant womenshould take 1000 micrograms each day. It is also strongly advised to ingestfolic acid fortified foods. Women who have already experienced pregnancy with neuraltube defects need to take a daily dose of 4,000 micrograms of folic acidsupplements.
Treatment
Most different types of neural tube defects cannot betreated at all, although survival and certain functions of infants affected byspina bifida and meningoceles may be improved by aggressive surgicalmanagement.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...