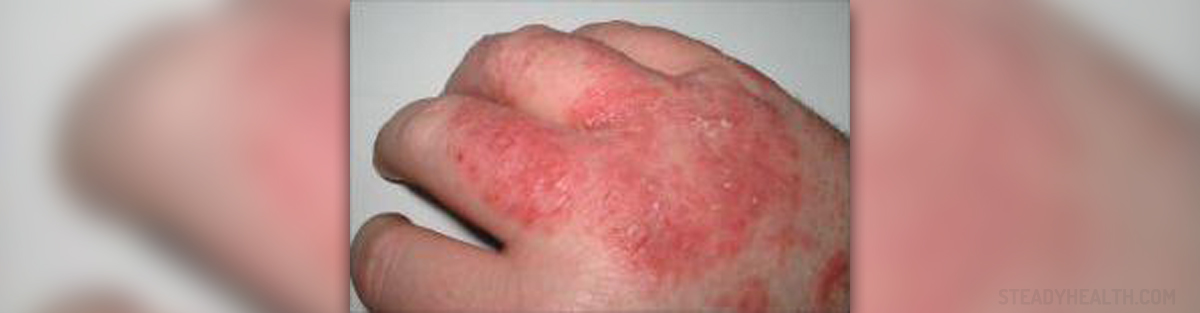
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a chronic condition characterized by very itchy rash made of bumps and blisters. The very name may make people believe that the underlying cause is Herpes virus. However, the condition has nothing to do with Herpes virus. The appearance of the skin changes is the reason for the name of the condition.
Dermatitis herpetiformis occurs in people who are 20 years of age and older. In some cases children can be affected as well. It is equally distributed among men and women. The actual cause of dermatitis herpetiformis has not been fully understood yet. However, it is in majority of cases associated with gluten sensitivity i.e. celiac sprue disease.
Clinical Characteristics of Dermatitis Herpertiformis
The leading sign of dermatitis herpetiformis is a typical rash. It is itchy and is characterized by chronic papulovesicular eruptions. These skin lesions are equally and symmetrically distributed on extensor surfaces such as the buttocks, back of the neck, scalp, elbows, knees etc. The size of the blisters is quite small and they are usually no bigger than 1 centimeter in diameter. The rash is very itchy and drives person to scratch skin lesions. By scratching many patients disturb the original appearance of the rash before coming to see a doctor.
Rash in dermatitis herpetiformis develops through three stages. Initially there is a slight discoloration of the skin. What follows is formation of obvious vesicles and papules. They gather in groups. The last stage is actually the healing stage when vesicles and blister disappear and the skin remains with specific discoloration (darker or lighter skin comparing to the healthy one).
Treatment for Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Diagnosis of dermatitis herpetiformis is confirmed with a blood test for IgA antibodies. Skin biopsy is of additional help in final setting of the diagnosis.
Dermatitis herpetiformis is treated with certain medications and dietary changes.
Many patients respond well to dapsone. For example, itching may subside 2-3 days after the drug has been administered. Still, since the condition generally originates from celiac disease it is essential to mention that dapsone has no effects on intestinal lesions. This is why, apart from medicamentous treatment, patents suffering from celiac disease must follow a strict gluten-free diet.
Dapsone is an antibacterial drug and the explanation of its efficacy in case of dermatitis herpetiformis has not been fully understood yet. Since its administration may cause different side effects during the treatment, patients undergo regular blood monitoring. Patients who cannot tolerate dapsone may be administered some of the following drugs: colchicine, lymecycline, nicotinamide, tetracycline, sufamethoxypyridazine or sulfapyridine.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...