From half genetic hearing loss forms, about 70% are said to be caused by recessive genes, about 15% have a dominant cause and 15% is left for other inheritance forms.
Most Common Forms of Genetic Hearing Loss
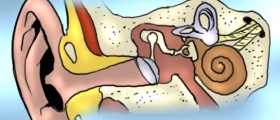
Genetic hearing loss can be divided in 2 categories. The Syndromatic hearing loss means that the hearing loss is accompanied by other clinical findings, and Non -Syndromatic category means just the hearing loss. Non –Syndromatic hearing loss is more common.
Most common form of genetic hearing loss is caused by a gene called Connexin 26 (CX26). Out of more than 400 known causes to genetic loss of hearing, CX26 resulted in 1/3 of the cases.Around 5% of all the hearing loss cases are dominant syndromatic. These include Waardenburg Syndrome, Branchio-Oto-Renal (BOR) Syndrome, Neurofibromatosis Type II (NFII), Stickler Syndrome and Treacher-Collins Syndrome.Waardenburg Syndrome can affect one or both ears. The side effects include white forelock, fussed eyebrow, mismatch in eye colour, premature gray hair, widely spaced eyes high nasal bridge, partial albinism and under developed nose tip.Neurofibromatosis Type II is a progressive sensorineural syndrome. It can lead to deafness. Spots on the skin, freckling and cataracts are common side effects. There is a possibility of acoustic tumors growing in the VIIIth cranial nerve that can cause the hearing loss. There is a possibility of tumors affecting other nerves.
Other Syndromatic Forms of Hearing Loss
Treacher-Collins Syndrome is a conductive, characterized by striking facial features. These include down slanting eye slit openings, unusual pupil openings, under developed cheek bones, cleft palate, malformed outer ears, narrow or absent ear canal, skin tags in front of the ear, balance problems and teeth alignment problems.
Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome can be conductive, sensoneural, or the combination of the both. Neck or area in front of the outer ear, can be covered in cysts or pits. Outer ear is known to be stapes fixed and malformed, inner ear may also be malformed or have enlarged vestibular aqueducts. One of the bigger concerns is linked to life threatening kidney (renal) problems.Stickler Syndrome is conductive in most cases. It is known to be sensorineural or mixed. Some cases are known to be progressive hearing losses. The Sticker Syndrome has 3 types. All three types are in relation with the altered expression of a collagen or connective tissue gene. These syndromes can be accompanied by downward placed tongue, cleft palate, progressive severe nearsightedness, small jaw, cataracts, under developed mid face, retinal degeneration and detachment, bone and joint disorders, early adult onset arthritis and malformation of middle ear bone.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...