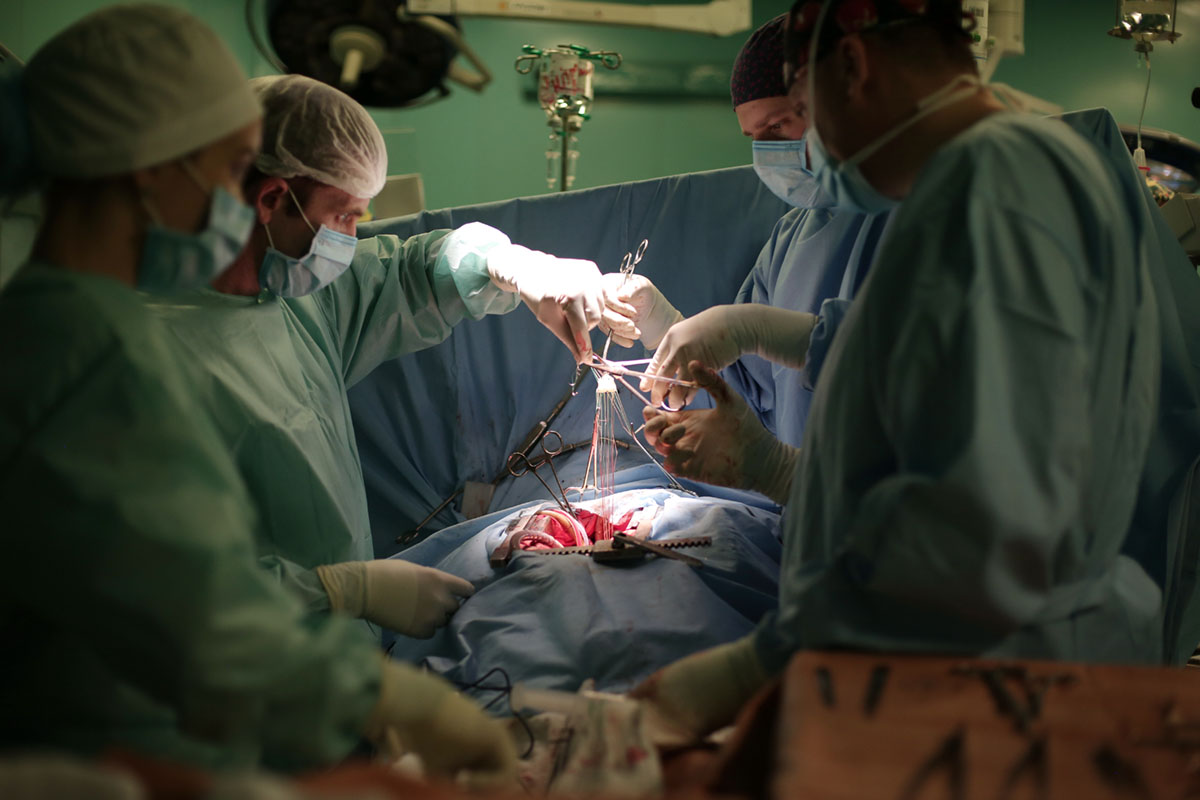
Aortic valve replacement is a cardiac surgery method in which a patient's failing aortic valve is replaced with an alternate healthy valve. The aortic valve can be affected by a range of diseases; the valve can either become leaky or partially. Aortic valve replacement is open heart surgery.
There are two basic types of valves when conducting this kind of operation, and those are tissue valves (usually made from animal tissues, either animal heart valve tissue or animal pericardial tissue. The tissue is treated to prevent rejection and calcification.) and mechanical valves (long-lasting and generally only one surgery is needed, but there is an increased risk of blood clots forming with mechanical valves. Recipients must usually take anti-coagulant drugs for the rest of their lives.)
The risk of serious complications from this type of surgery is usually stated as being between 1-3%, depending on the age and overall health of the patient, and the skill of the surgeon. Older patients, as well as more fragile ones, sometimes cannot be operated on because of elevated risks.
Complications
Although, it is considered to be a safe method, some complications may occur. They may be short-lasting, but they also may be more permanent. However, they are treatable with the right kind of prescribed medication.
Minor ones are skin numbness, bruising, nausea accompanied by vomiting, painful scar formation, atrial fibrillation, etc. The patient’s doctor should know how to deal with every one of these.
Major complications are not that common, but very serious when appear. One’s general health plays a great role when it comes to developing these complications. If any such case presents itself, a person should address their physician.
These are a possible stroke, heart attack, an infection, valve replacement failure and serious bleeding problems. Also, some patients experience other problems, nerve damage, kidney failure and even allergic reactions to medications.
The most serious of the major complications are rupture of the heart wall, which may lead to cardiac arrest, pneumonia, and lung failure.
If the complications are not noticed in time, they may lead to other, maybe untreatable problems, in which case one might need a blood transfusion, a pacemaker, dialysis or repeat surgery.
That is why it is of the utmost importance that one is checked regularly by a physician to see if any problems have occurred or complications have become present. He can spot the problems and find the solutions before they grow and cause irreparable damage.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...