What Is Cancer?
Cancer is a group of diseases that begin with the body’s cells. There are more than 100 types of cancer but abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells is what they all have in common. These cells are called cancerous cells or malignant cells. Healthy cells multiply only when the body needs them while abnormal cells continue dividing until they create a mass of extra tissue. This tissue is known as tumor or growth. It can be malignant (cancerous) or benign (non cancerous).
Colon Cancer
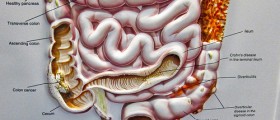
Colon cancer is a type of cancer that originates in the colon. Cancer of the colon is also called colorectal cancer. The colon is an organ of the digestive system, which has several functions such as digestion of food, absorption of nutrients and storage of fecal mater.
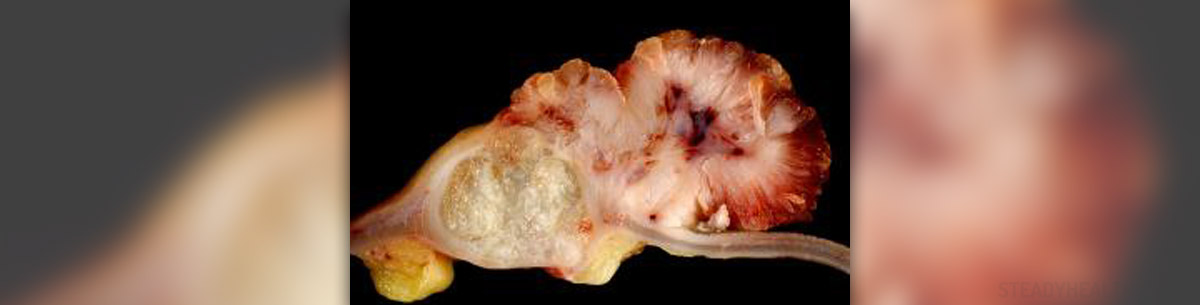
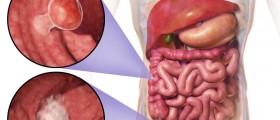
The colon along with the rectum forms the large intestine and cancers of the colon and rectum begin in the inner lining of the large intestine. Polyps are non cancerous growths of the large intestine but they have a potential to become malignant if they are not removed. In fact, in most cases, colon cancer develops from polyps.
Colon cancer tends to grow and affect nearby organs and lymph nodes and eventually spread to distant organs such as liver or brain. The spreading of colon cancer is called metastasis of the colon. Metastatic colon cancer can not be cured but the treatment can help to relieve the symptoms and prolong the patient’s life. On the other hand, colorectal cancer that is detected early can be cured. Therefore, knowing the early symptoms can help to identify colon cancer in its initial stage when it is treatable.
Early Symptoms of Colon Cancer
There are various and nonspecific symptoms that can indicate colorectal cancer. For instance, fatigue, weakness and shortness of breath often accompany cancer of the colon since the tumor can lead to iron deficiency anemia. Change in frequency or appearance of bowel movements is also a symptom of colon cancer. The disease can cause narrow stools, diarrhea, constipation or other changes in bowel habits. Constipation can result out of intestinal obstruction caused by large tumor. Persistent nausea and vomiting are often present too.
Blood in the stool originates from the growth located near the end of the colon or rectum. Unexplained weight loss is also caused by colon cancer. Bloating can be caused by a growth located toward the end of the colon.
Colon cancer can cause abdominal pain or cramps if there is a bowel obstruction. Blockage of the bowel prevents intestinal content to pass through and may cause severe pain and cramping. Perforation of the bowel due to a tumor can produce intense pain and it requires immediate medical attention.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...