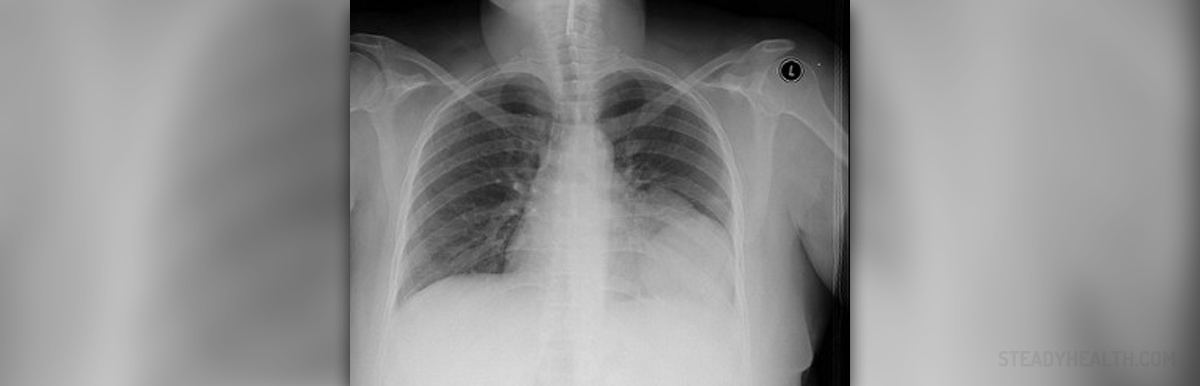
Bronchitis and emphysema often occur at the same time and the term Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease refers to the restriction of the airflow that result from either of these conditions. About three million people suffer from the disease, with many more cases remaining undiagnosed. It mainly occurs in those over forty years old and the risk increases with the aging process.
In severe cases, medications like steroids, antibiotics and mucolytics may be used, but the most vital thing with regard to treatment is to ensure that the patient ceases smoking. Smoking is the most common cause of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and therefore in order to prevent or reduce the onset of the condition, it is advised to avoid or quit smoking. The chances of developing the condition can be as high as 1 in 4 for smokers. Those who have never smoked almost never develop COPD.
Working or inhabiting highly polluted areas might also lead to COPD. Air pollution will certainly worsen the condition and also increases the risk of developing COPD. Some people are at risk of developing COPD as a result of some inherited genetic conditions, such as protein deficiency.
Symptoms
Coughing, breathlessness, increased mucus production, weight loss, tiredness and ankle swelling are all indicators of the presence of COPD. Coughing can become chronic and is normally the first outward sign of COPD. Breathlessness will gradually occur more often over the years, especially if you continue to smoke. Chest infections will also be a common occurrence if you do develop COPD. These infections will worsen all the symptoms of COPD that are associated with the airways. Some people may also experience haemoptysis (the coughing up of blood) as a result of COPD.
Unlike asthma, COPD causes permanent damage to the airways; treatment will only limit the symptoms rather than cure the disease. There are several other differences between COPD and asthma, but it is possible to suffer from both conditions, so it is important to recognize these differences. If you are waking up at night due to breathlessness or wheezing, this is more likely to be a symptom of asthma.



,-Asthma-And-Anxiety_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...