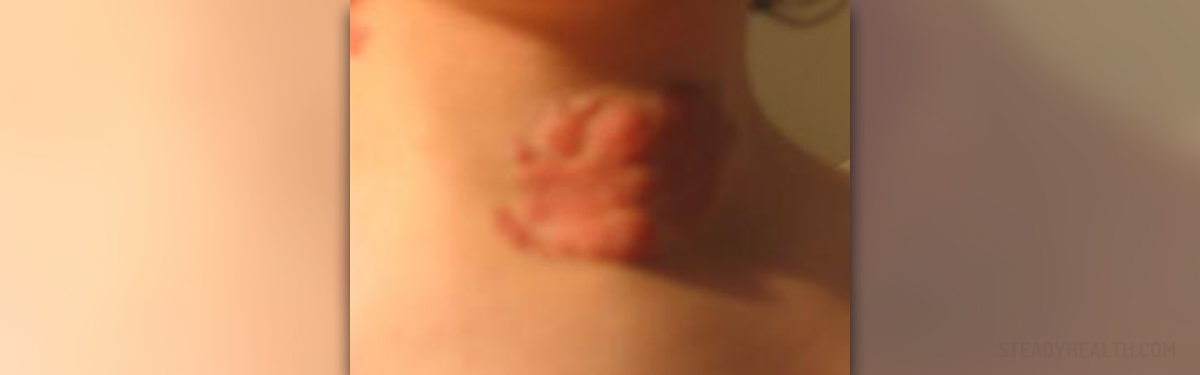
Neurofibromatosis is an autosomal genetic disorder and it features with the growth of specific tumors called neurofibromas. The disease may affect any part of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and all other nerves in the body. This genetic disease is generally diagnosed in childhood and early adulthood. Neurofibromas are benign tumors. Still, their growth may interfere in normal functioning of the affected organs and organ systems.
There are two types of the disease, type 1 neurofibromatosis (also known as Von Reclinghausen disease) and type 2 neurofibromatiosis. These types differ according to the place of gene mutation and they generally feature with different symptoms and signs.
Symptoms and Signs of Neurofibromatosis
Type 1 neurofibromatosis features with two or more neurofibromas on the skin or under the skin or one plexiform neurofibroma. These patients have specific freckling of the groin or the arm pit. Café au lait spots are pigmented spots and a typical feature of this type of neurofibromatosis. The diagnosis can be set only if there are at least 6 spots from the time of birth. There are also skeletal abnormalities and lisch nodules. Patients suffering from type 1 neurofibromatosis may also develop an optic glioma, hypertension and epilepsy and suffer from learning or speech problems.
Neurofibromatosis type 2 features with bilateral tumors and acoustic neuromas of the vestibulocochlear nerve. Neuromas eventually cause hearing loss and additional problems include headache, vertigo, problems with balance and facial weakness or paralysis. Patients suffering from type 2 neurofibromatosis may also develop brain and spinal tumors.
Diagnosing Neurofibromatosis
Diagnosis of neurofibromatosis is set after thorough physical examination of a patient. The specific sings of the disease are crucial for setting of the diagnosis. Additional tests and exams include lab studies of mutation analysis, imaging studies such as MRI of the brain and spinal cord which confirm the presence of tumors. Wood lamp examination is required to confirm the presence of specific skin spots and slit lamp examination confirms the presence of Lisch nodules.
Treatment for Neurofibromatosis
The patients are monitored for complications and the treatment begins once the complications start to occur. The child undergoes regular tests and examinations such as examination of the skin for new neurofibromas and the development of the old ones. Blood pressure is measured regularly as well. The child's growth and development are under thorough scrutiny so that any skeletal changes or abnormalities may be reported on time. And finally, it is necessary to evaluate learning development and progress in school.
In some patients there is a need for surgical removal of tumors which cause compression to nearby tissues or damage the surrounding organs. Patients suffering from vestibular schwanoma may benefit from stereotactic radiosurgery. Plastic surgery as well as laser therapy are helpful in removal of the skin tumors and may improve patient's appearance.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...