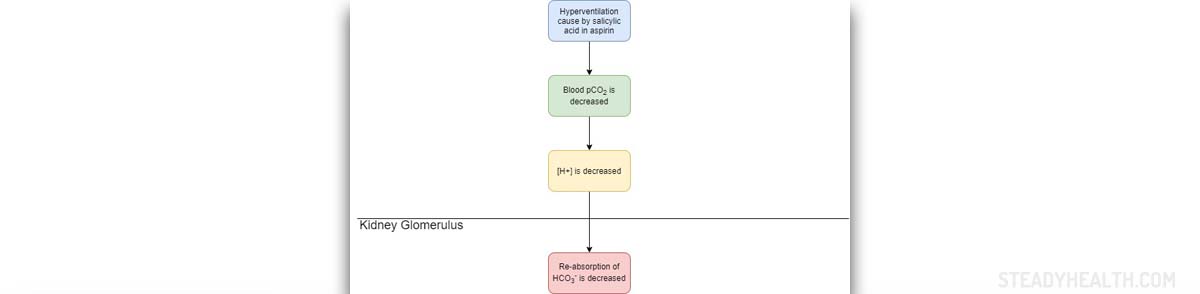
Metabolic Alkalosis
Metabolic alkalosis is a medical condition which features with increase in HCO3. Compensatory increase of Pco2 may or may not be present and pH can be elevated or in some cases normal. Metabolic alkalosis is in most cases caused by excessive and prolonged vomiting, hypovolemia, and uncontrollable usage of diuretics and reduced level of hypopotassemia. If left untreated metabolic alkalosis can eventually lead to severe headaches, lethargy or tetany. The diagnosis can be set after clinical examination and certain laboratory tests. The goal of the therapy is to bring the imbalance under control and to find the actual cause of metabolic alkalosis and to treat the cause as well.
Symptoms and Signs of Metabolic Alkalosis
Mild forms of metabolic alkalosis are asymptomatic. In serious cases the increased protein binding of ionized Ca++ causes hypocalcaemia and this eventually causes headaches and lethargy. The muscles are highly excitable so that tetany develops. Delirium or seizures are possible as well. Even the function of the heart is jeopardized and the patient may develop serious arrhythmias or anginal symptoms. Weakness is a consequence of hypopotassemia.
Causes of Metabolic Alkalosis
Loss of hydrogen ions can be one cause of metabolic alkalosis. Hydrogen can be lost in prolonged vomiting or due to excessive excretion by the kidneys. In some cases the loss of water in the extracellular space leads to dilution and increased concentration of bicarbonate. This is caused by diuretics.
In some patients retention of bicarbonate may be a cause of metabolic alkalosis. Hypokalemia is regularly accompanied by metabolic alkalosis. And, certain alkalotic agents may be another cause of this medical condition. Namely, bicarbonate that is administered in patients who are suffering from peptic ulcer and hyperacidity may cause metabolic alkalosis if given in large doses.
Diagnosis of Metabolic Alkalosis
ABG and serum electrolytes are tested. Basically the doctor can set the diagnosis after clinical examination of the patient. And finally, in some cases measurement of urinary Cl- and K+ are performed.
Treatment of Metabolic Alkalosis
The doctor will search for the underlying cause and treat it. This way metabolic alkalosis can be successfully brought under control. The doctor especially pays attention to potential hypovolemia and hypopotassemia.
In case of Cl- responsive alkalosis the patient is administered 0.9% saline solution intravenously. The desirable results are achieved when urinary Cl rises to certain level and urinary pH comes back to normal level.
In patients who are suffering from serious metabolic alkalosis hemofiltration and hemodyalisis may be helpful, especially in case of volume overload and evident problems in function of kidneys.




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)










Your thoughts on this
Loading...