
Surgery to remove all or part of stomach or to bypass it as means of loosing weight is likely to cause what is known as dumping syndrome, or rapid gastric emptying. It is a condition where the undigested stomach contents (food and gastric juices) move on (get dumped) into small intestine too soon and in an unregulated manner.
Typical symptoms of dumping syndrome include stomach cramps and nausea and can be mild or severe. Most people suffering from this condition feel the symptoms soon after the meal, while others experience symptoms two to three hours after eating.
True downsides of dumping syndrome include unhealthy weight loss and malnutrition, fear of eating, fear of going out as there is no toilet nearby and even difficulties in social life, such as problems on job that may even lead to loss of job.
Who is affected
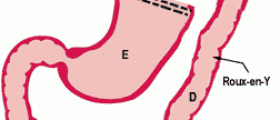
Dumping syndrome occurs in 25%-50% of patients that have undergone gastric bypass surgical procedure, with at least mild symptoms. Symptoms appear within weeks or immediately after return to a regular diet. It is more likely to occur and more likely to be severe if greater portion of the stomach has been removed or bypassed. It is also accepted that gastrointestinal hormones play a role in development of dumping syndrome.
Sometimes, the dumping syndrome becomes a chronic condition.
Procedures that carry risk
Some surgical procedures are usually associated with increased risk of developing rapid gastric emptying syndrome. Among these are:
GastrectomyThis is a surgical procedure which removes all or part of the stomach and usually includes removal of the pylorus.
GastroenterostomyThis is a surgical procedure used for bypassing of the pylorus by directly connecting the stomach to the small intestine beyond the pylorus. This procedure is sometimes used on people suffering from stomach cancer.
VagotomyThis is a surgical procedure wherein some innervation to the stomach is cut, in order to reduce levels of acid that the stomach produces.
FundoplicationThis is a surgical procedure that is sometimes performed on people with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Upper portion of the stomach is wrapped around the lower section of the esophagus so that thus applied pressure to the esophagus reduces the reflux of gastric content into it. In rare cases, unintended damage to some stomach nerves during the surgery can cause dumping syndrome.
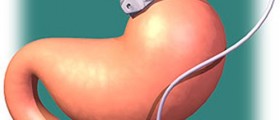
Gastric bypass surgeryThis surgical procedure is used against morbid obesity. Its goal is to create smaller stomach than before and disable to person to eat as much as before the operation, thus leading to weight loss.
Conditions that carry risk
There are conditions and medications that increase risk of developing a dumping syndrome. These include diabetes, cyclic vomiting syndrome and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Known troublesome medication is metoclopramide.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...