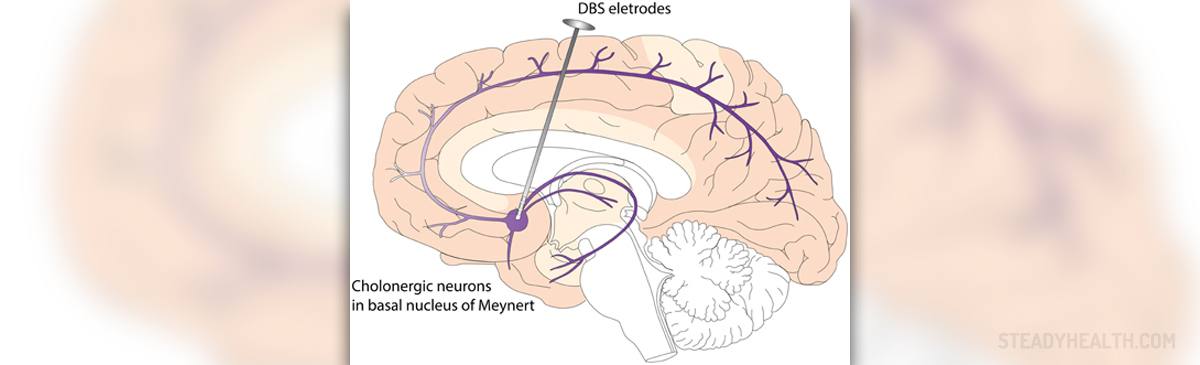
Introduction
Dementia is a condition that futures with the loss of the cognitive ability. It can be caused by a variety of illnesses such as neurodegenerative conditions and vascular disorders. Furthermore some forms of dementia are present in certain inherited diseases. Even infections can be the cause of dementia. This mental impairment usually affects elderly people. However, dementia can occur in younger patients as well.
Causes of Dementia
The leading cause of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. In these patients progressive and irreversible changes in brain lead to deterioration of cognitive ability and memory loss.
Dementia develops in another disease called Lewy body dementia. In this condition specific changes affect different areas of the brain. Unlike Alzheimer's dementia this form of dementia is usually more rapid.
Pick's disease is a neurodegenerative disease presenting with destruction of nerve cells in the brain. In majority of patients frontal lobe as well as temporal lobes is most commonly affected. The disease is progressive and leads to the atrophy of the affected areas.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease are also related to dementia. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis belongs to a group of neurodegenerative diseases. It features with the changes of motor neurons. Additionally rather drastic and severe cognitive impairments are present in Huntington's disease as well as in progressive supranuclear palsy.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is incurable brain disease in which the normal brain tissue is replaced with the damaged one which resembles sponge. All the brain functions are impaired and one of the symptoms includes quick development and progression of dementia.
Infections such as HIV or AIDS can also lead to dementia. People who are suffering from these horrible conditions tend to develop dementia in terminal stages of the infection.
If a person has experienced multiple strokes the chance of getting dementia increases. Apart from dementia these people suffer from additional mental impairments.
Chronic alcoholics usually end up with dementia. The real cause lies in deficiency of B1 vitamin and chronic destruction of brain cells caused by alcohol. Alcoholics are more susceptible to brain injuries which can also lead to dementia.
Drug addiction and chronic usage of certain medications are other possible causes of dementia. The development of dementia is connected to the usage of anticholinergics, barbiturates, digitalis, benzodiazepines and certain antidepressants.
Even certain infections including neurosyphilis, meningitis and encephalitis may result in dementia. Still this happens rather rarely and mostly if the brain tissue is permanently damaged by the infection.
Dementia can be one of the symptoms of brain tumors. And finally cognitive function can be damaged by prolonged metabolic abnormalities.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...