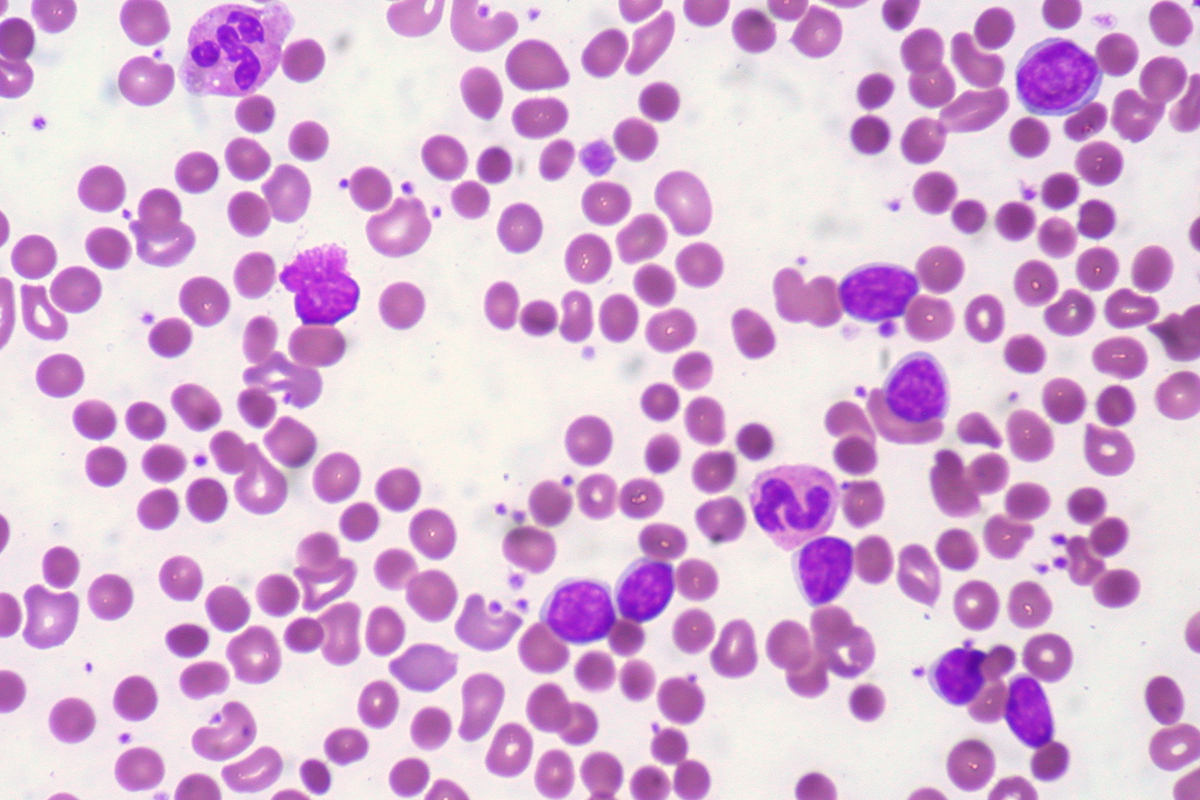
Anemia of chronic disease is a different-degree anemia that occurs due to certain chronic illnesses. This type of anemia ranges from mild to moderate and generally affects patients suffering from chronic non-infective illnesses or malignant tumors.
Anemia of chronic disease develops approximately a couple of months after the onset of the primary medical condition. It may be asymptomatic and found accidentally or it is intensive enough to cause certain symptoms and signs. Anemia of chronic disease is generally normocytic-normochromic but it can also be normocytic-hypochromic and normocytic-hyperchromic.
Clinical Characteristics of Anemia of Chronic Disease
As it is the case in other types of anemia anemia of chronic disease is either asymptomatic (only if it is mild) or it leads to characteristic symptoms and signs such as pallor, fatigue, general weakness, chest pain and in severe cases shortness of breath. The symptoms and signs of anemia accompany the symptoms and signs of the primary illness so we can only discuss a variety of combinations depending on the very disease that has led to anemia. What are Causes of Anemia of Chronic Disease?
There are many illnesses such as chronic infections, inflammatory diseases and malignancies that can induce anemia. Anemia results either from the very condition or due to treatments used for symptoms and signs of these illnesses.
This type of anemia commonly occurs in people suffering from different autoimmune disease (Chron's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis etc.) and cancers (particularly leukemia and lymphomas). Furthermore, anemia of chronic disease is common among patients with chronic kidney disease, those suffering from liver cirrhosis, long-term infections (chronic bacterial endocarditis, osteomyelitis). Anemia also develops in HIV patients and those suffering from hepatitis C and B.
Diagnosing Anemia of Chronic Disease
This type of anemia is diagnosed the same way as other types. The insufficient number of red blood cells is easily confirmed with a simple blood test. The doctor examines the level of hemoglobin, red blood count, reticulocyte count, serum ferritin and serum iron.
Treatment for Anemia of Chronic Disease
In case of mild anemia patients may not require any treatment at all and the condition improves when the underlying illness is brought under control. However, moderate and severe forms of anemia of chronic disease must be properly treated.
Moderate forms of anemia of chronic disease require iron supplements and only in severe cases and serious form of anemia the person receives blood transfusion. Patients suffering from chronic kidney disease generally receive shots of a specific medication called erythropoietin. Erythropoietin is an essential substance for proper production of red blood cells.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...