Heart failure may manifest through tachycardia, venous congestion and low cardiac output. When the left ventricle of the heart starts failing, breathlessness may occur, becoming more severe gradually. All in all, heart failure is a serious, life-threatening condition which needs to be treated medically as soon as possible.
Facts about Heart Failure
Numerous factors may be involved in the diagnosis of heart failure. For example, the New York Heart Association observes the relation between the symptoms of this condition and the effort involved in their genesis. On the other hand, the American Heart Association adds the progression of any heart diseases into the requirements for the diagnosis.
Either way, laboratory studies involved in the diagnosis need to encompass a full-scale blood test, analysis of electrolytes, kidney and liver functions and a 2D echocardiography. All these tests are necessary for a primary evaluation of one's proneness to heart failure. A chest radiograph may be necessary too, giving various pieces of information about the condition of the heart and the surrounding organs.
Treatment for Heart Failure
When it comes to acute heart failure, the patient's condition needs to be stabilized before any other steps can be taken. Then, the condition needs to be diagnosed, along with the etiology and precipitating factors. The main initial goal is stabilizing the condition, relieving the patient's symptoms.
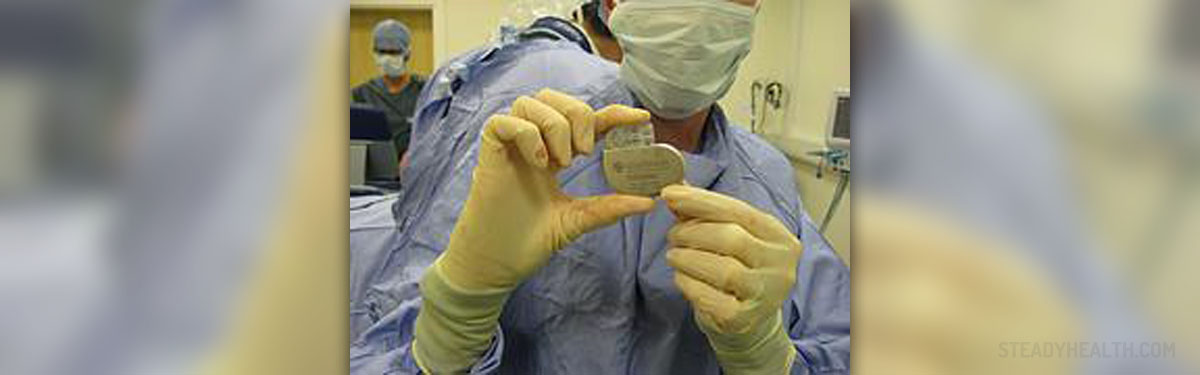
If a surgery is necessary, heart transplantation, coronary artery bypass grafting, valve repair or replacement, ventricular restoration or cardiac resynchronization therapy may be the possible options, depending on the condition.
Medications are used in order to prevent the symptoms and complications of heart failure, reducing morbidity. Diuretics, digoxin, inotropes, oxygen and morphine all may be involved in heart failure therapy.
The human body possesses mechanisms which defend it from heart dysfunction and failure. However, when these mechanisms fail to maintain the optimal performance of the heart, acute heart failure takes place.
If the stress on the walls is chronic and intense, myocyte hypertrophy, death and regeneration may be the responses of the body. The fatal outcome could be countered by lowering the stress on the heart wall. However, effective ways of achieving this in patients suffering from heart failure is something that is still being worked on.
Calcium overload may lead to heart failure and death, triggering arrhythmias beforehand. Any decrease in the hearts blood input and output can, furthermore, lead to heart dysfunction and, possibly, failure. Water retention may be a possible side-effect of a heart failure, leading to further engagement of the heart. Yet, numerous medical experts are researching the above mentioned ability of the heart to renew itself.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...