Cytomegalovirus is a member (i.e. a viral genus) of herpesvirus family. It can cause a viral infection in humans and initiate severe damage to certain groups of people particularly unborn children.
Acute Cytomegalovirus Infection Causes and Risk Factors
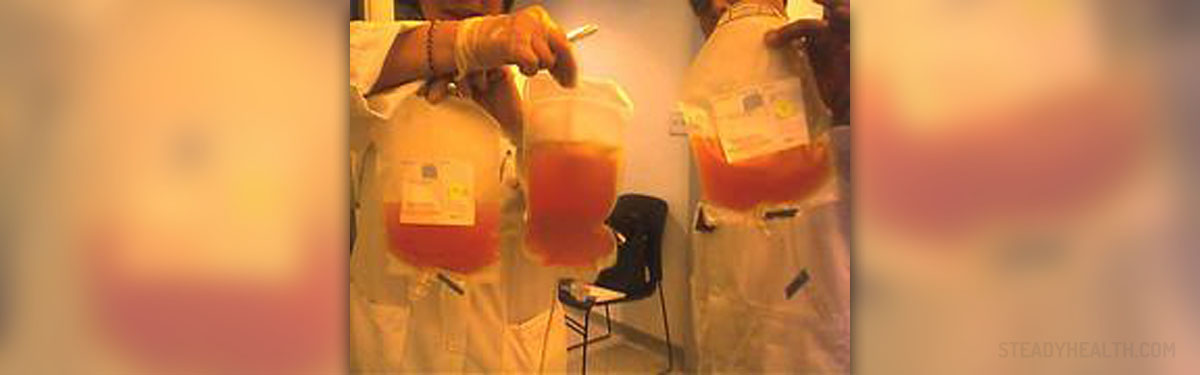
Cytomegalovirus infection is quite common and can be contracted by blood transfusions and organ transplants. Spread of the virus is also achieved by respiratory droplets and sexual contact.
Even though many individuals get exposed to the virus at some point in their lives, it is those with weak immune system who are more likely to develop the infection. In some cases people infected with cytomegalovirus develop a mononucleosis-like syndrome.
It is estimated that cytomegalovirus infection most commonly affects people between the age of 10 and 35. More severe and complex form of the infection is present in people with weak immune system.
Acute Cytomegalovirus Infection Clinical Characteristics
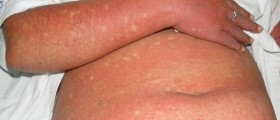
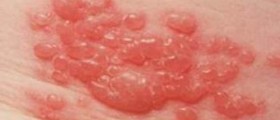
Cytomegalovirus infection leads to fever, fatigue, malaise, loss of appetite, neck lymphadenomegaly, muscle ache and rash. Sore throat is another potential symptom patients complain about.
Additional, but not so characteristic symptoms include chest pain, cough, irregular or rapid heart beat and shortness of breath. Patients may also report headaches, be sensitive to light or develop hives. Neck stiffness and swelling of the liver/spleen affect only small number of patients.
Diagnosing Cytomegalovirus Infection
Apart from taking medical history and physical examination, it is important to perform special lab test like blood tests for platelets and white blood cells, chemistry panel, liver function test and monospot test. The presence of the virus is confirmed with a CMV (cytomegalovirus) ELISA antibody test and CMV serum PCR test.Acute Cytomegalovirus Infection Treatment
Majority of the infected, previously healthy individuals recover within 4-6 weeks without any specific treatment.
Treatment basically includes plenty of rest and symptomatic treatment. Antiviral medications are administered only to immunocompromised people.
It is estimated that after approximately 10 days fever goes away and enlarged lymph glands return to their normal size in around 4 weeks. Fatigue is the only symptom that lingers for several months.
Potential Complications
Cytomegalovirus infection is associated with many complications such as colitis, neurological complications, heart complications (pericarditis or myocarditis), lung complications (pneumonia), and in individuals with enlarged spleen there is chance of organ rupture.
Prevention of the infection is achieved by avoiding close or intimate contact with the infected person (one should abstain from kissing and unprotected sexual contacts).
When it comes to organ transplants and blood transfusions, donors are thoroughly checked and tested for the presence of virus which prevents potential transmission of the infection.












-And-Multiple-Sclerosis-Differences-And-Similarities_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...