Apnea of Prematurity - Overview
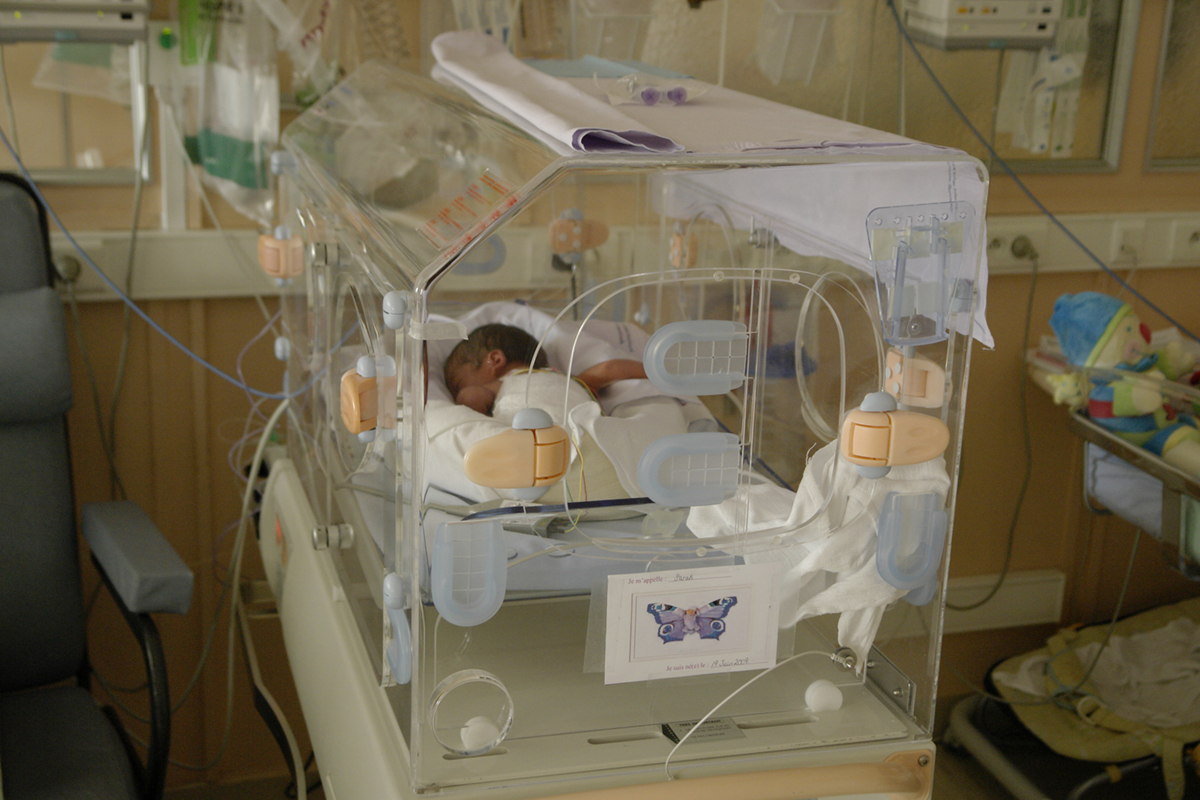
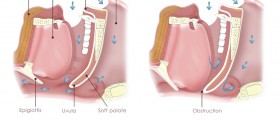
Apnea of prematurity is cessation of breathing in prematurely born babies. This breathing cessation lasts for more than 15 seconds and is typically accompanied by either hypoxia or bradycardia. The problem can be easily explained. Namely, in premature babies the specific part of the brain and spinal cord in charge with breathing has not fully developed and cannot allow non stop breathing. This is why sudden and occasional episodes of shallow or stopped breathing occur.
If a well experienced doctor diagnose the condition prior mother and a baby are discharged from the hospital. The symptoms of apnea of prematurity usually occur after 2 days of life and may last to 3 months. In majority of cases the condition withdraws spontaneously.
During hospitalization the problem may be noticed by well experienced nurses. Children suffering from apnea of prematurity are monitored with the assistance of cardiorespiratory monitor. The condition is typically accompanied by cyanosis and bradycardia. All the changes are due to be noted. Pulse oximetry measures the intensity and duration of oxygen desaturation. It is essential to define the type and severity of the condition. All the cases of apnea of prematurity can be classified into mild, moderate and severe. Unlike mild and moderate apnea of prematurity, severe form of the disease requires vigorous stimulation, administration of increased concentration of oxygen and assisted ventilation. The doctors must exclude all other causes of apnea before setting a definitive diagnosis of apnea of prematurity.
Treatment for Apnea of Prematurity
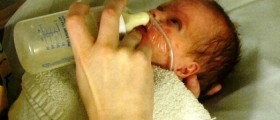
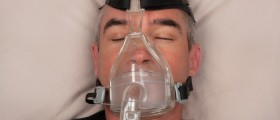
If premature infant develops this type of apnea he/ she will receive medical care in the hospital's intensive care unit. The breathing is assisted with a ventilator and certain medications. The baby is intubated and the air is blown inside the baby's lungs. The ventilator is basically programmed to provide with a specific number of breaths per minute. Baby's breathing as well as heart rate and oxygen levels is thoroughly monitored. Once the infant is disconnected form the ventilator he/ she requires further assistance with breathing in a form of nasal continuous positive airway pressure. In this case the machine provides with sufficient amount of oxygen and the baby breaths on its own. The goal of medicamentous therapy is to accelerate maturation of baby's lungs.
In some cases babies are discharged from intensive care unit with an apnea monitor. The sensors of this device measure the chest movement and breathing rate and alarm if there are certain abnormalities. It is essential for all parents to be taught how to use apnea monitors and how to respond to the alarm. Parents are additionally taught cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The doctor decides how long the baby should wear the monitor and when it is no longer necessary.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...