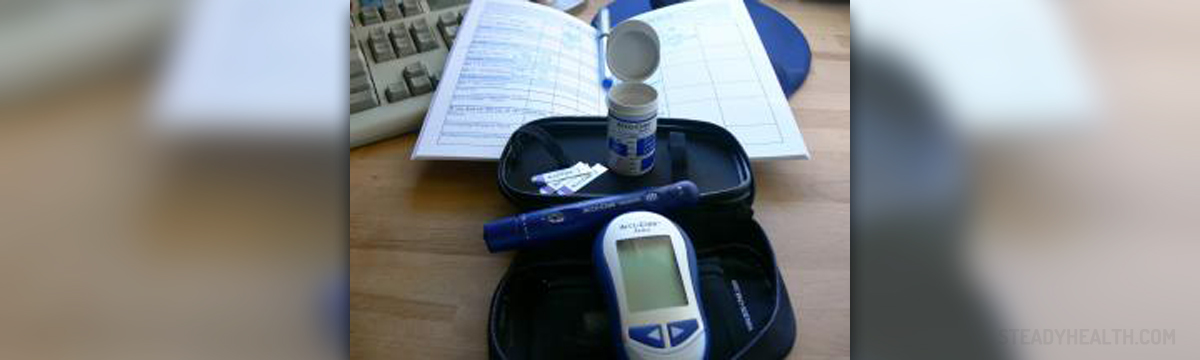
Gestational Diabetes-Overview
Diabetes is a term that refers to a group of the metabolic diseasesin which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does notproduce enough insulin (a substance that is needed for the sugar to enter thecells), or because the cells do not respond to the insulin produced even thoughthere is enough of it. There are three types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, andgestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which women who havenot been previously diagnosed with diabetes exhibit high blood glucose (sugar)levels during pregnancy (most often, during the second half of the pregnancy). Thisis a temporary condition and it may go on its own as soon as the mother hasgiven birth. However, in few cases, it can lead to these women developing type2 diabetes in later life.
Gestationaldiabetes affects two to four per cent of all pregnant women.
Causesand Symptoms
Duringpregnancy, the body produces a number of hormones to sustain the pregnancy.However, some of these hormones can impair the action of insulin in thetissues, and by doing this, raise the blood sugar levels in the body. Expertsstill do not know why some women develop gestational diabetes, and some do not.
Formost women, this condition causes no noticeable symptoms. Rarely, it can causeexcessive thirst or excessive urination. But, these symptoms are usuallywritten off as being a normal part of the pregnancy. However, it is importantthat a pregnant woman have regular check-ups with her doctor, so he may run thenecessary tests and determine whether she is in risk of having gestationaldiabetes.
TreatmentPlan
Gestational diabetes treatment options are limited as it is thoughtnot to be a very complicated disorder. Mostly, diet adjustment is recommendedto pregnant women. Another option for treatment is insulin injections when itis not controlled by the diet.
Thetreatment plan that is proven to be very effective when it comes to dealingwith gestational diabetes includes the following:
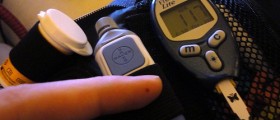
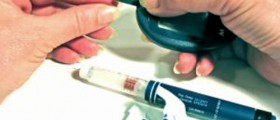
Regularcheck-ups. If a woman goes to the doctor’s regularly, he will be able to spotthe disease in its infancy and the treatment will be far more efficient. Hewill also recommend that the patient check the blood sugar levels twice a day.This is also a good way of spotting this condition early.Eatinga balanced diet. A dietitian should be consulted. And a diet plan that he makesshould be followed strictly.CheckingFetal Growth. This is important, because if the growth of the baby is more thannormal, one might require insulin shots to keep the blood sugar levels normal.Exercisingregularly. In this way, the body gets the help needed to utilize the insulinand control the excess amount of blood sugar in the blood. Exercises should beperformed for about two and a half hours per week.Insulin shots. This is only performed if the blood sugar is not under control after following a planned diet and exercises.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...