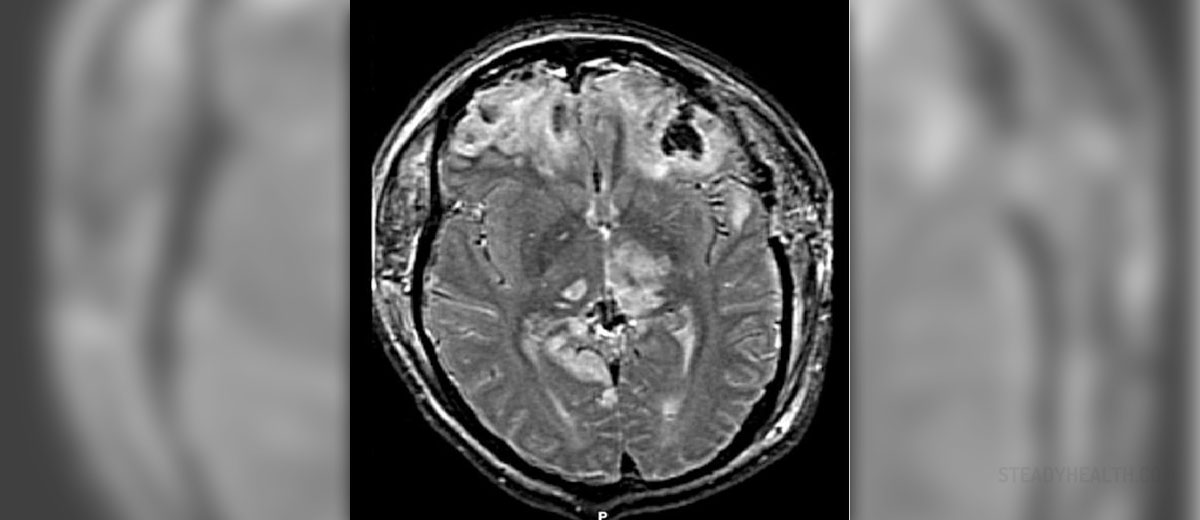
Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injury occurs as a result of the external force which causes trauma to the head and the brain. The symptoms of traumatic brain injury may vary depending on the intensity of the force and the actual damage to the brain tissue. If left untreated traumatic brain injury may cause serious complications including lethal outcome.
Symptoms of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Mild injury of the brain and its structures is classified as concussion. The symptoms of concussion are usually subtle and they vary a lot. Loss of consciousness may occur and last a few minutes or it does not have to happen at all. In mild injury of the brain the patients are typically dazed for a while and they get back to normal spontaneously.
In mild injury, the brain is only shaken inside the skull and there is no interruption of its integrity. Blood vessels as well as meninges are not damaged. The function of the brain stops for a few seconds after the injury but they are all restored without any consequence.
Early symptoms of mild traumatic brain injury include confusion and/or temporary memory loss, headache, tinnitus, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting. Loss of consciousness may occur and it usually does not last longer than 30 minutes.
In some patients symptoms may develop a certain period after the injury and they are classified as delayed or secondary symptoms. Some of them are mood swings, problems with concentration and memory, headaches and migraines. Patient may additionally complain about sensitivity to light and sounds, changes in smell and/or taste and problems with balance and coordination. Depression and insomnia may occur as well.
Symptoms of Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
In moderate and severe traumatic brain injury symptoms are intensive and more dangerous. They are classified into immediate and delayed symptoms. Immediate symptoms include loss of consciousness that lasts more than 30 minutes, dizziness and drowsiness. Patients are confused, they may vomit and complain about headache and ringing in the ears. Problems with vision include complete loss of vision or just blurred vision. Pupils may be dilated or even asymmetric which may point to severe injury of the brain. In extreme cases patients develop slow pulse and slow breathing.
Delayed symptoms are more dramatic. They include slurred speech or complete inability to speak and serious problems with thinking. Patients commonly suffer from amnesia and some of them develop seizures. In severe injury patients may become comatose, paralyzed and lose control of the bladder and bowel.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...