Genetic disorders are those caused by abnormalities in the genes or chromosomes. In most cases, these abnormalities are caused by defective genes inherited from the parents. Changes in the chromosomes, such as chromosomal aberrations or absence or presence of entire chromosome may also cause genetic disorders.
- Single gene inheritance
- Multifactorial inheritance
- Chromosome abnormalities
- Mitochondrial inheritance
There are over 4.000 different genetic diseases identified so far, but scientists and doctors are still unable to prevent them. To this day, we can detect some of genetic abnormalities in unborn children by ultrasound and some other medical techniques and methods. People allover the world suffer from genetic disorders. Some of the most common genetic disorders are Down syndrome, Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, sickle cell anemia and galactosemia.

Down Syndrome
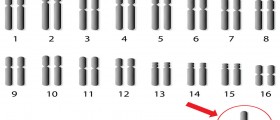
Down syndrome is a developmental disorder, caused by additional copy of chromosome. Patients suffering from this syndrome have a flat face and broad nose and their appearance is very distinctive. Many of children with Down syndrome are mentally challenged and they are exposed to higher risk of respiratory infections, hearing and visual problems, leukemia and heart related conditions.
Life expectancy of these patients is usually reduced by 50 years. Corrective surgery and physical and speech therapy may help these patients.
Scientists have discovered that mothers older than 35 years of age more often gave birth to children with Down syndrome. Ultrasound may detect this syndrome in an unborn child.
Huntington’s Disease
This genetic disorder affects the speech, thought and movements. First symptoms usually appear in people in an age group of 30 to 50-year-olds and the condition progresses, causing more problems. Patient suffering from Huntington’s disease needs constant medical care and drugs, but with physical and speech therapy he can lead a normal life.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s affect the functioning of the brain, memory, thought and language. This condition usually affects older people. Patients start to lose the ability to think or remember anything. Although there is no cure for this disease, medications may slow down the progression of the symptoms.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Red blood cells become rigid in this type of anemia. They normally transport oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body, but because of the rigidity, there is less oxygen transported to important organs in the body. Heart, kidneys, liver, spleen and lungs get less oxygen than they need so patients experience anemia, jaundice and growth problems.
In most cases, patients suffering from this genetic disorder live 30 to 40 years. The most common treatment options are blood transfusions, plenty of water and avoidance of exercise and stress.
Galactosemia
Galactosemia is caused by the lack of enzyme known as GATL. Because of that, they can’t metabolize galactose from the milk or dairy products. Accumulated galactose may cause enlarged liver, kidney failure and retardation. Dietary restrictions early in the life may prevent these complications, but the patients must avoid milk and dairy products for the rest of their lives.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...