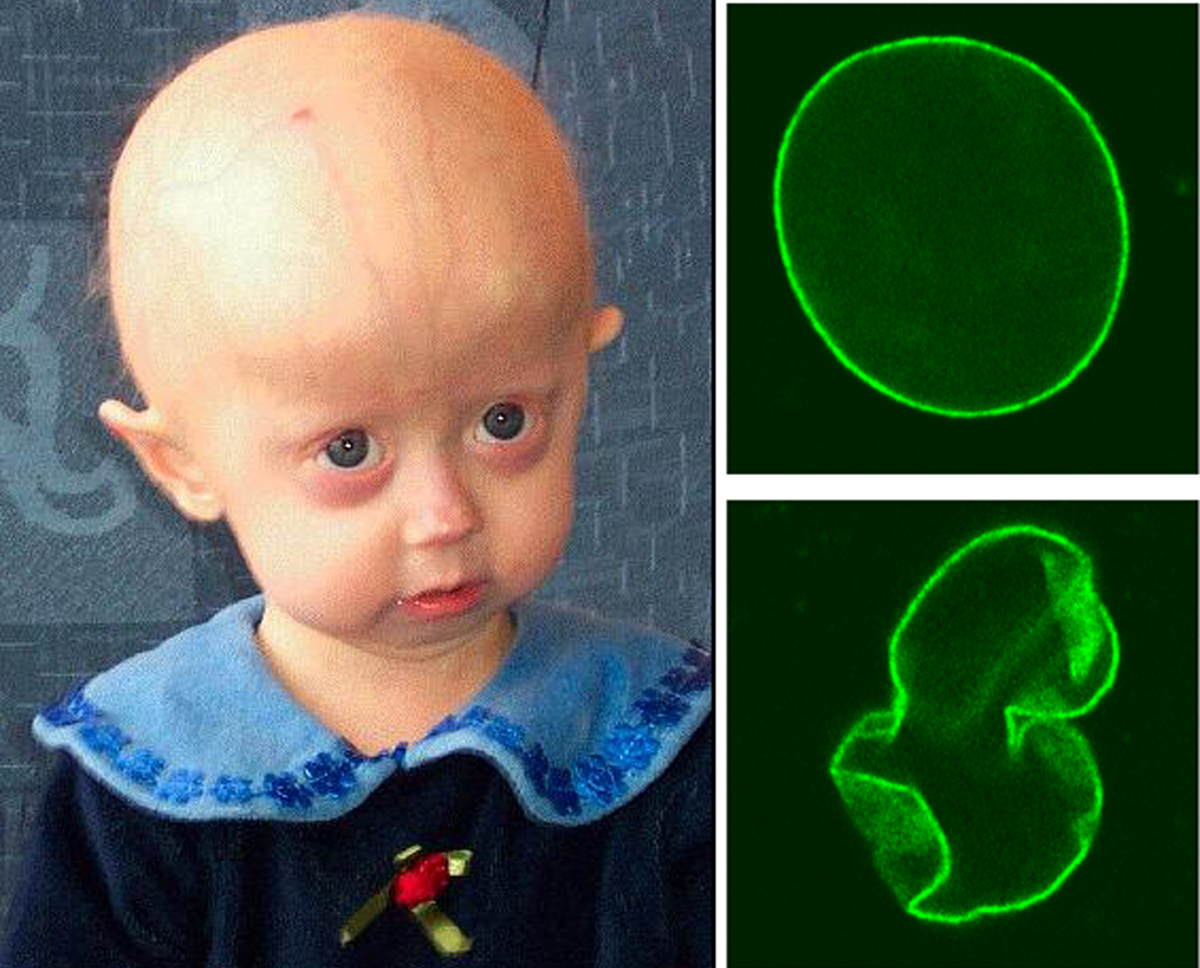
Clinical Characteristics of Progeria
During the first year of life a child suffering from progeria shows noticeable retardation in growth. The height and the weight of the child are way below average comparing to his/her peers. Still, motor and mental development are not jeopardized and they normally continue.
Further progression of the disease is associated with slow growth, hair loss, hardening of the skin of the trunk and extremities. Such patients have a narrow face with beaked nose and a small lower jaw. The head appears to be too large comparing to the rest of the body. The eyes are prominent and the voice is high-pitched. There are also problems with teeth and joints (stiffness of joints and potential dislocation).
Potential complications in patients suffering from progeria include severe atherosclerosis and accompanied illnesses such as cardiovascular problems or stroke, cataract, tumors and insulin resistance.
Therapy for Progeria
Unfortunately, since it represents a genetic disorder, progeria is incurable. Since these patients are prone to many other illnesses and complications they require constant monitoring and adequate treatment. Complications of atherosclerosis (cardiovascular disease) are treated conservatively or surgically (artery bypass surgery etc.). Low-dose Aspirin can prevent fatal complications such as heart attack or stroke. Teeth problems are related to premature growth of permanent teeth. This is why it is good to extract primary teeth before the permanent start to grow and in this way prevent overcrowding.
Physical and occupational therapy are very efficient when it comes to joint stiffness. With regular physical and occupational therapies a child may remain active and function and move on his/her own. These children are prone to weight loss. Therefore their diet should be rich in calories. Babies who cannot eat properly are fed with the assistance of feeding tubes. Cataract and tumors require specific treatment.
Even though the condition is devastating for both, the child and the parents, the parents must cope and make a lot of effort in order to help their child. There are support groups where they can get additional information about the condition and meet other people with the same problem. And finally, continuous consultations with the doctor are essential for helping the child.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...