GIST (gastrointestinal stromal tumor) represents a rare type of sarcoma affecting various parts of the digestive system, predominantly the stomach. It is estimated that approximately 6 out of 10 GISTs originate from the stroma of the stomach. The rest affects other parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The tumor is rarely found outside the digestive system.
GIST most commonly affects people between 50 and 70 years of age. The reason why tumor develops in the first place remains unknown. However, some medical conditions such as neurofibromatosis make the person more susceptible to GIST.
GIST Clinical Characteristics
In early stages the tumor is quite small, hence it does not cause any symptom. Only when the disease progresses sufficiently and tumor increases in size placing pressure to the nearby structures, patients turn to their doctors.
Majority of patients complain about pain/discomfort in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness, nausea and fatigue. Sometimes one may notice blood in stool or the stool becomes darker due to bleeding from the upper portions of the gastrointestinal tract. Bleeding is also a cause of anemia, another potential characteristic of the disease.
Treatment for GIST
Treatment for GIST depends on the stage of the disease i.e. many factors some of which are the size and location of the tumor and patient's overall health.
Apart from standardized treatments like surgery, radiation therapy or target therapy, some patients are advised to engage in clinical trials. Clinical trials offer treatments with new drugs and a combination of already existing therapies.
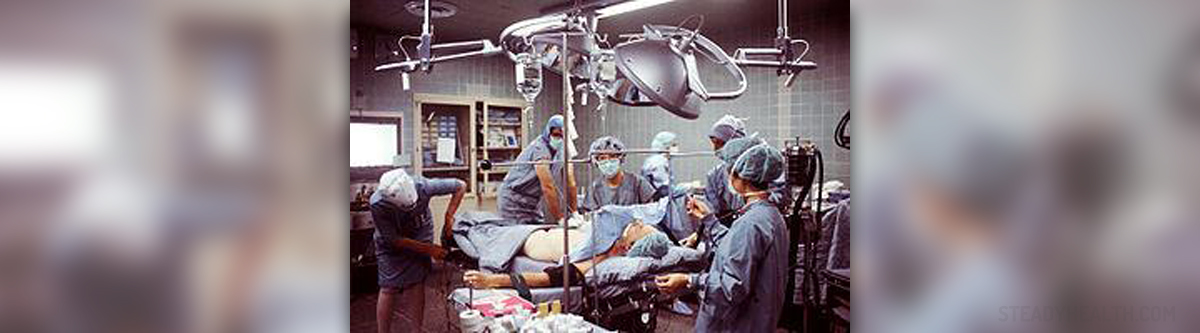
Localized GIST can be surgically removed. Surgery is a treatment option that needs to be performed whenever possible. It removes the entire tumor or reduces the size of it. If the tumor has already infiltrated the nearby organs, patients first undergo specific medicamentous treatment and if the tumor shrinks, they are additionally operated. Even when the tumor is completely removed, there is chance of disease recurrence and this is why patients require frequent check-ups.
Target therapy for GIST comprises imatinib, a drug approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This is a highly potent medication, improving the prognosis of the disease in many patients. The drug is administered even in case of complete spread of the tumor to various tissues in the body. If the tumor continues growing in spite of treatment with imatinib, patients may be prescribed another drug called sunitinib.
Radiation therapy is not a frequently used treatment in people suffering from GIST. However, it can be applied as so called palliative treatment to reduce pain and control symptoms in people in whom the disease has significantly progressed.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...