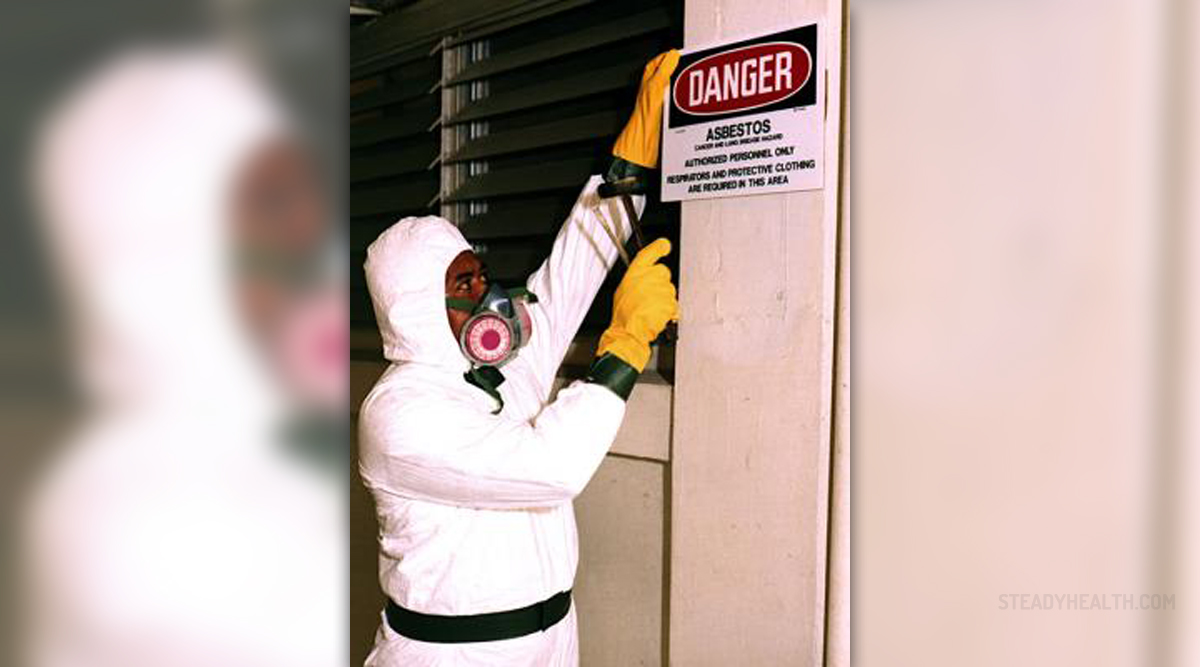

Asbestos is a complex of six naturally occurring minerals, known by its high heat resistance. This property of asbestos made it very popular in the late 19th century among manufacturers and builders. The asbestos was mixed with cement or woven into fabric or mats and then used in buildings. It was used commercially in North America since the late 1800s, and especially during the World War II. In 1989, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency banned all new uses of asbestos; however, uses developed before 1989 are still allowed. The reason behind this decision is that asbestos is a serious health threat to humans, as it can cause cancer and many other related lung diseases.
Health effects of asbestos
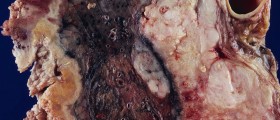
Asbestos is composed of separable, long and thin fibers, which are very small and can be seen only under the microscope. Any kind of disturbance to the surfaces containing asbestos can cause the fibers to float in the air. Humans are always exposed to small levels of asbestos from the air, but health disorders normally occur only when they are exposed to very high concentrations. However, the first symptoms of excessive asbestos exposure may sometimes show up even 30 years after the initial contact. This happens because humans normally expel most of the inhaled fibers, but some of them can become lodged in the lungs and may remain there throughout the lifetime. Accumulation of fiber causes scarring and inflammation, affects one's breathing capacity and gradually leads to diseases.
Symptoms of asbestos exposure
As already mentioned, the symptoms of asbestos exposure may not become apparent for many years after the exposure. Anyone who has been exposed, or suspect they have been exposed to asbestos should seek medical attention and carefully monitor changes in the body for associated symptoms. Most of the patients will have general problems with breathing, such as shortness of breath, wheezing or hoarseness. Patients will also suffer from a persistent cough that will become worse over time. One of the severe symptoms is the blood in the fluid coughed from the lungs. The sensation of tightening or pain in the chest is also very common. Patients often feel difficulty swallowing accompanied with the loss of appetite and associated weight loss. Swelling around the neck or in the face are also common, as well as are fatigue or anemia.
The only way to diagnose asbestos exposure is to undergo a thorough physical examination, including a chest x-ray and lung function tests. A lung biopsy can also detect small inhaled particles of asbestos in the lung tissue.






_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...