
The primary purpose of the vitamin D is to strengthen the bones and provide proper functioning of the whole organism. If there is an imbalance of this vitamin in the body, it can lead to various health disorders such as rickets, osteoporosis, muscle pain and cramps and kidney disorders.
The human body requires a certain level of vitamins in the body. Vitamins are nutrients that can be divided into 13 types. These types can be classified into two groups of vitamins - those that are soluble in water and those which are soluble in fat.
Vitamin D belongs to second group. For humans, the most important are vitamin D2 and D3, which together are called calciferols.
Fish, eggs, cheese, butter milk, cod liver oil and fortified milk are the foods that are rich in vitamin D. It is important to enter the optimal amount of this vitamin, because its surplus and its lack both can have negative consequences.
The main function of vitamin D is to allow proper absorption of calcium and phosphorus in bone. It performs this function by encouraging the bowel to absorb minerals from imported food.
There are various studies by which it is proved that vitamin D has a positive effect on the prevention of osteoporosis, high blood pressure and cancer. Also, there are indications that this vitamin plays an important role in strengthening the immune system and ensuring the proper functioning of the nervous system, but it is necessary to undertake more researches in this field.
The optimal daily dose of vitamin D is 5 mcg for people aged 1-50. With age optimal dosage is increased. Besides food, the sun can be a good source of vitamin D. Just 15 minutes of sun exposure 3 times a week provides the necessary quantities of vitamin D to the body.
Negative effects of vitamin D are reflected in its absence and overdose. Surplus of this vitamin causes excessive absorption of calcium from food, which leads to disturbances in the functioning of the heart, lungs, blood vessels and kidneys (polyuria, nocturia, polydipsia and renal failure).
High level of vitamin D in the body can lead to the formation of kidney stones which can cause severe pain. Excessive doses of this vitamin can also cause nausea, migraines, anxiety, mental retardation, convulsions and muscle atrophy, hypertension and heart diseases.
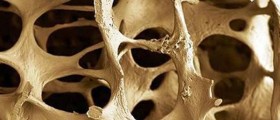
As a consequence of a lack of vitamin D occurs rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults. Rickets means the fragility of bones and their susceptibility to fractures and deformity. Osteoporosis involves a reduced bone density, which causes weak bones and fractures. Osteoporosis occurs mainly as a consequence of age or menopause in women.
Lack of vitamin D also can cause osteomalacia, which means the weakening of muscle with osteoporosis.
As a result of decreased level of vitamin D also can develop insomnia, weight loss, pain in bones and muscles and decrease immunity.
To fulfill the requirements of the organism for this vitamin and to keep its level in balance the most important is quality nutrition, physical activity and generally healthy lifestyle.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...