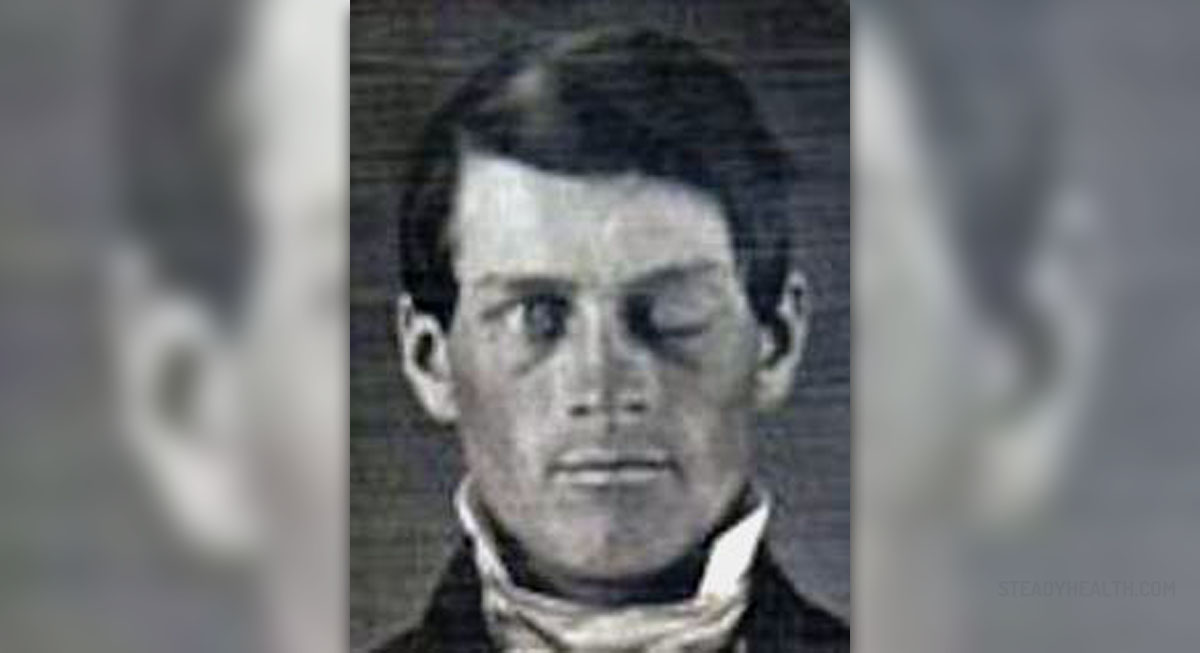

Ptosis is a condition which features with pathological dropping of the eyelid which becomes obvious if one is looking straight ahead. It occurs due to improper functioning of one or both muscles which are in charge with lifting of the upper eye lid. This condition can be congenital or acquired. It may also run in families.
Symptoms of Ptosis
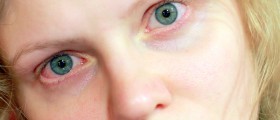
The very patient notices changes in the level of the upper eyelids. One of the eyelids is lower than the other. This is particularly noticeable when one is looking straight ahead. The patient may look sleepy. Patients are trying to lift the affected eyelid by frowning and this may eventually cause headache. Headache, however, is not regular symptom of ptosis. In severe form of ptosis, one's vision can be seriously obstructed and the only way for these patients to open the affected eye is to do it manually.
Complications of Ptosis
Definitely the most serious complication of ptosis in children is amblyopia. Amblyopia or lazy eye causes ignoring of the images which are sent to brain from the affected eye and favoring images received from the healthy eye. A lazy eye can be surgically corrected only if the surgery is performed before the age of 8. After that the loss and impairment of vision is irreversible due to complete development of visual paths.
Ptosis interferes in regular daily activities and bothers people particularly when they are driving, reading etc. In children it may also cause emotional problems. And one more complication of ptosis is headaches located in the frontal part of the skull.
Causes of Ptosis
Ptosis can be classified as congenital and acquired. In 50% of children suffering from congenital ptosis the exact cause of the condition cannot be identified. In other 50% of congenital ptosis causes may be related to other developmental conditions (blepharophimosis syndrome), conditions affecting the nerves of the face and eyelids, birth trauma, different muscular conditions (myasthenia gravis) and pseudoptosis.
Acquired ptosis is further divided into involutional ptosis, neurogenic ptosis, myopathic ptosis, mechanical ptosis and ptosis caused by trauma.
Involutional ptosis is caused by weakening of the tissue around the eyes. In neurogenic ptosis the problem is related to the nerves which inervate the eyelids. Myopathic ptosis is caused by muscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis. Mechanical ptosis is usually caused by a growth, lump of swelling of the eyelid. And finally, a variety of trauma to the eye and accompanying injuries may lead to ptosis due to damage of different tissues.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Ptosis
Ptosis can be easily diagnosed by well-experienced ophthalmologist. Certain tests are performed to identify the underlying cause of ptosis. Children are additionally examined because there is chance they have developed a lazy eye.
Mild ptosis does not require treatment at all. In mild congenital ptosis children are monitored. Moderate and severe forms of the disease require surgical correction. And finally, ptosis may be sometimes treated by certain medication which bring the underlying condition under control and consequently reduce the degree of ptosis.







-In-Infants-And-Older-Children_f_280x120.jpg)




Your thoughts on this
Loading...