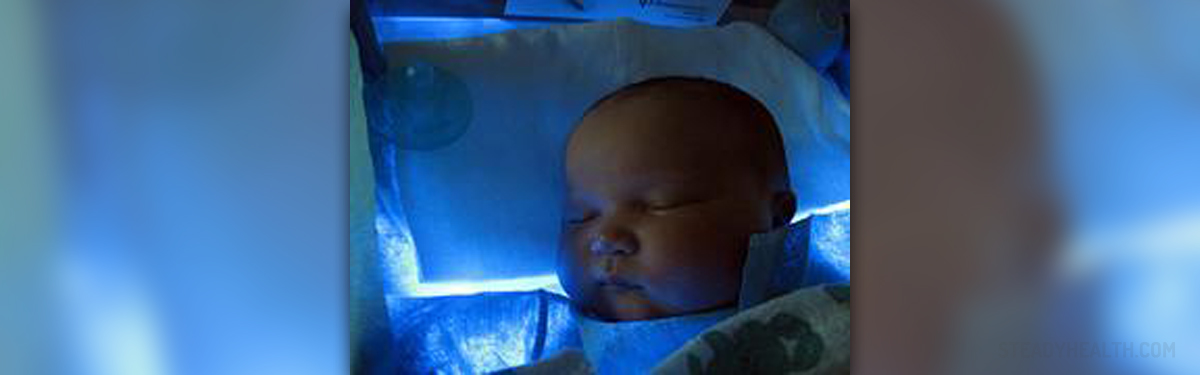
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), also known as erythroblastosis fetalis is a life-threatening condition caused by incompatibility between the blood types of the mother and the baby.
Causes of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
Hemolytic disease of the newborn occurs when the mother’s antibodies attack red blood cells of the baby. This condition is most commonly seen when an Rh negative mother conceives a child with an Rh positive father and the baby inherits Rh antigen from the father. When the mother’s antibodies cross the placental barrier and enter the fetal circulation it results in HDN.
This usually takes place during pregnancy or at delivery but may also occur during miscarriage, termination of pregnancy, trauma, medical procedures like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling all of which rupture the placenta or in any other situation when blood cells of the mother and the baby mix.
In such events, the immune system of the mother recognizes Rh positive red blood cells from the baby as foreign. The mother’s immune system reacts by producing the antibodies that attack and destroy the red blood cells from the baby. When the immune system from the mother encounters incompatible antigen for the first time, it stores the antibodies to attack the foreign cells if they appear again in subsequent pregnancies. This is called Rh sensitization.
Rh sensitization does not occur during a first pregnancy but affects Rh positive babies from future pregnancies. The condition is called erythroblastosis fetalis if it develops during pregnancy, and in newborns it is known as hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Symptoms of Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
Hemolysis occurs when the antibodies originating from the mother destroy the baby’s red blood cells. This causes anemia in the newborn and results in increased production of red blood cells by the bone marrow, liver and spleen. This leads to enlargement of these organs. The newly formed red blood cells are usually immature and fail to function as normal red blood cells.
Due to break down of red blood cells the level of bilirubin raises. However, as the infant cannot eliminate bilirubin, it accumulates this substance in the blood and other tissues and fluids in the body (hyperbilirubinemia). This leads to jaundice or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Some infants may develop kernicterus, the severe form of hyperbilirubinemia that causes accumulation of bilirubin in the brain and leads to deafness, seizures, brain damage and death.
Prevention of Hemolytic Disease of the NewbornHDN can be easily prevented thanks to prenatal testing. In early pregnancy women undergo blood tests to determine whether they are Rh negative. Rh negative women that are not sensitized receive a drug called Rh immunoglobulin around 28th week of pregnancy. The second dose of the drug is given 72 hours after childbirth.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...