
A postpartum hemorrhage is diagnosed by observing the amount of blood a woman loses during the postpartum stage, either while the placenta is still being delivered or afterward (primary postpartum hemorrhage happens within the first 24 hours after giving birth, while secondary postpartum hemorrhage can happened up to six weeks postpartum). If you lost over 500 ml of blood, postpartum hemorrhage will be diagnosed.
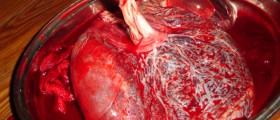
There are various reasons women can have a postpartum hemorrhage, including failure of the uterus to contract after delivery, injury during birth, a retained placenta (placenta that will not come out) and blood clots. Blood loss should always be monitored by your midwives or OBGYN, but women should also take note of blood loss especially heavy bleeding in the weeks after birth. Pitocin artificial oxytocin, which is also used for labor induction is one of the ways to get a postpartum hemorrhage to stop.
Massaging the uterus can be one of the measures taken too. A blood transfusion is needed in cases where a woman lost more than 2000 ml of blood during her postpartum hemorrhage, and if you are in the hospital, you will generally be transferred to theater in case more radical measures like a hysterectomy (removing the uterus) become necessary. Quick action is necessary in cases of postpartum hemorrhage, since a very large amount of blood loss can occur in a frighteningly short amount of time.
- www.who.int/reproductivehealth/topics/maternal_perinatal/pph-woman-trial/en/
- www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/Ch6_16PPH.pdf
- Photo courtesy of Master Sgt. Nick Choy, 142nd Fighter Wing Public Affairs via: www.airforcemedicine.af.mil/News/Display/Article/1617869/oregon-airmen-respond-to-hurricane-lane-during-summer-training-in-hawaii/











Your thoughts on this
Loading...