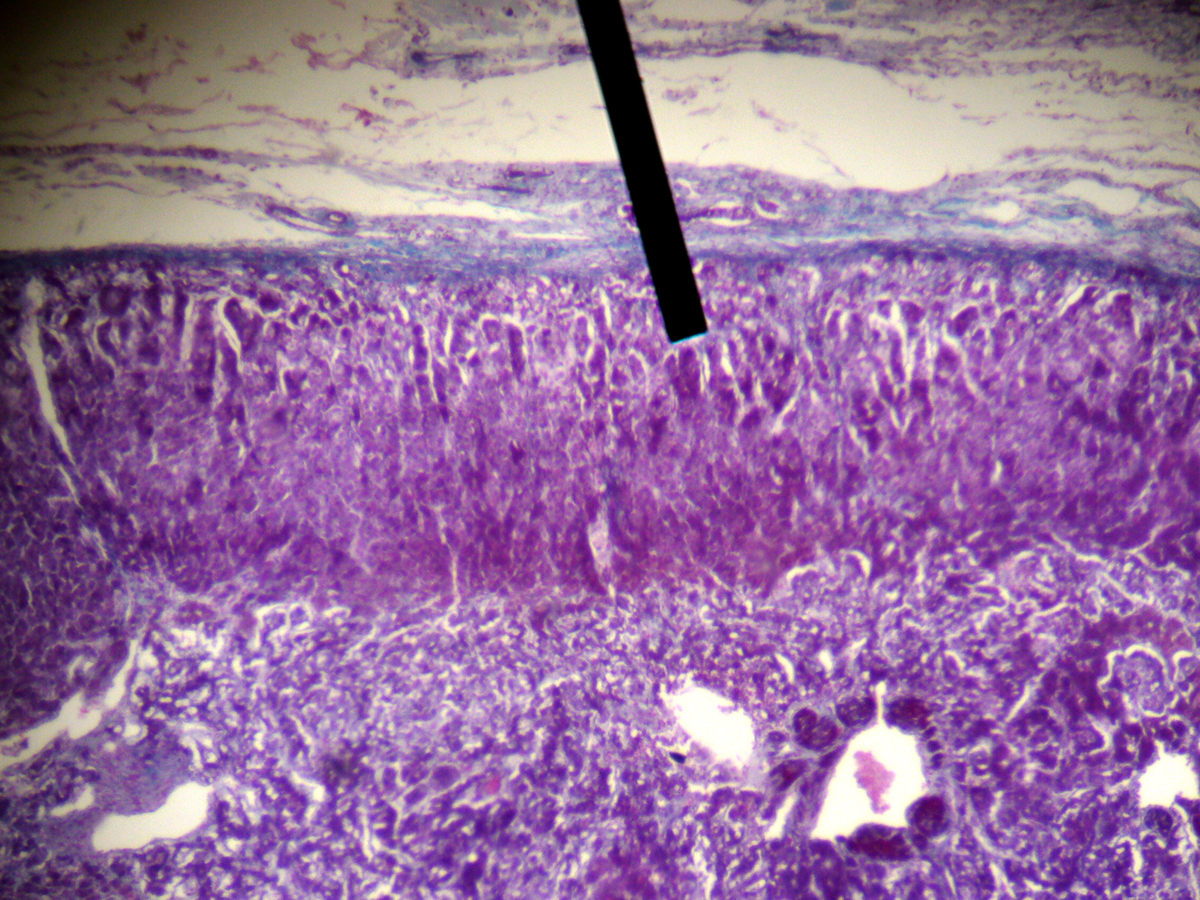
Addison's disease is a disorder that develops due to inadequate function of the adrenal glands. These glands are situated on the top of both kidneys and play a significant role in production of different hormones and a couple of neurotransmitters. In case they do not function properly and practically stop producing all the hormones they are in charge of, the person develops Addison's disease. Such patients may have extremely low levels of cortisol and aldosterone.
The disorder affects both genders and people of all ages and may be easily treated with hormone replacement therapy. Left untreated, the condition soon leads to serious imbalance of hormones and associated processes in the body, which may be life-threatening.
Addison's Disease is Hormonal Disorder
As it has already been mentioned this is a condition associated with abnormal production of a few hormones. The medulla of the gland is responsible for production of adrenaline-like hormones, the ones that act like neurotransmitters. The cortex of the gland, on the other hand, synthesizes glucocorticoids, minerelocorticoids and androgens. The first two are vital for life and their absence is highly detrimental. The member of glucocorticoids, cortisol, is an important hormone that participates in a variety of processes. It allows us to convert food fuels into energy and is a part of the immune system's inflammatory response. This is the hormone that saves us from stress. Aldosterone is a member of mineralocorticoids. The hormone is the one that maintains optimal balance of sodium and potassium in the body. By doing so, aldosterone plays a role in management of adequate level of blood pressure. Finally, in patients suffering from Addison's disease there is insufficient amount of androgens. These hormones are essential for sexual development and their lack is not life-threatening but still requires proper treatment approach.
Addison's disease may be a consequence of direct damage to the gland (primary adrenal insufficiency) or develops due to abnormalities affecting the pituitary gland, the gland that controls functions of the adrenal glands. In primary adrenal insufficiency the adrenal glands are structurally changed in such a way that they simply cannot produce required hormones. The damage may be triggered by an autoimmune disease or is associated with tuberculosis, different other infections of the adrenal glands, primary/secondary tumors of the adrenal gland or bleeding into the gland. In case of secondary adrenal insufficiently the gland is practically intact. Still, there is absence of stimulation by the pituitary gland. Under normal circumstances the pituitary gland synthesizes ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), the one that boosts the adrenal glands to produce certain hormones. Absence of such stimulation results in insufficient amounts of practically all hormones of the adrenal gland. Secondary adrenal insufficiency is also possible to occur if one takes corticosteroids for a long period of time.
All in all, the absence or lack of hormones produced by the adrenal gland may trigger many health complications. Addisonian crisis is the most severe one. Namely, it predominantly develops once the person who suffers from undiagnosed Addison's disease is exposed to extreme physical stress, is injured or develops some infections or illnesses. In this case patients develop a constellation of symptoms all of which develop due to severe adrenal insufficiency.
Treatment for Addison's Disease
The goal of the treatment for patients with primary adrenal insufficiency is to substitute all the missing hormones and those that are not produced in sufficient amounts. This is relatively simple treatment requiring taking medications on a daily basis. Cortisol is replaced with oral Hydrocortisone tablets. This medication is taken twice per day and this way allows the body to maintain desirable levels of cortisol throughout the day. Optimal amount of aldosterone is also achieved with oral medications called fludrocortisone acetate. This drug is taken once per day. Patients in whom the level of aldosterone is low are also advised to increase daily intake of salt.
Patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency have normal levels of aldosterone therefore, they need not replacement of this hormone. However, they need Hydrocortisone and the dose of the drug may be increased during intercurrent illness when one is most susceptible to addisonian crisis. The dose is for instance, increased during acute febrile illnesses, after trauma, injuries etc.
Addisonian crisis is a life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical help and immediate treatment. The goal is to bring low blood pressure, low glucose level and high level of potassium under control. Doctors routinely administer intravenous injections of Hydrocortisone, saline and dextrose, all of which bring rapid improvement of many imbalances.
In case patients suffering from Addison's disease need to undergo some surgical procedures under general anesthesia they receive injections of Hydrocortisone and saline prophylactically. These medications are administered the night before the surgery and may need to be repeated until patients become capable of taking oral forms of the drugs.
And finally, no matter how frightening Addison's disease may appear, it is an easily manageable disease that only requires timely diagnosis and optimal treatment. Even though patients need to take medications for the rest of their lives, they lead normal lives and these drugs do not have any detrimental side effects or interfere with other bodily functions.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...