People react to drugs in two distinctive ways, either by common and predictable reactions or in some unpredictable way. A person may experience some known side effects, interactions of the drugs he or she is taking or unwanted effects because of the overdose of the drug. On the other hand, some people may experience unexpected adverse effects, intolerance to the drug, as well as immunologic or allergic reactions to administered medication.
Unusual reactions to medications are not rare and they occur in 15 to 30% of all hospitalized patients, but just one out of every 10 unintended reactions to drugs is a true allergic reaction.
How to Recognize Allergic Reaction to Drugs?
In most cases, people who are allergic to some medication did not have that reaction the first time they used this drug. It appears after at least one week of use and it is different than any expected side effect, suggesting it might be an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis. Once the patient stops taking the drug, effects usually wear off after several days.
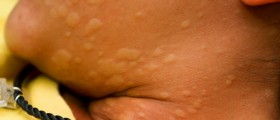
The most commonly noticed symptoms of an allergic reaction are skin rashes in a form of urticaria and angioedema. Immunologic reactions not related to allergies often cause sun-burn like reactions, peeling and blistering of the skin. Some conditions can be very serious and even life-threatening problems, like Steven-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Frequent Drug Allergies
Antibiotics, such as penicillins and cephalosporins are well known to cause allergic reactions in some people. About 10% of all people experience some “allergic reaction” to penicillin and some even experience severe problem - anaphylactic shock after the use of this drug. If you ever experienced allergy to penicillin drug, make sure to say that to your doctor and get tested for this allergy. Cephalosporins are less likely to cause allergic reactions than penicillin but if you are allergic to penicilins, you might also be allergic to these drugs as well.
Other medications, such as sulfonamides, diuretics or oral anti-diabetic drugs may also cause reactions very similar to allergies. NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as naproxen, ibuprofen and Aspirin are also associated with allergic reactions and with non-allergic hives, swelling and anaphylaxis. Intravenous contrast dyes can also lead to allergic reaction and this is why doctors advise using antihistamines and oral steroids before the procedure with these dyes. Medications used to treat seizures (epilepsy) can lead to non-allergic reactions, causing rash, hepatitis or body aches.
Local and general anesthetics can both cause true allergic reactions, but these complications are much more common in patients undergoing general anesthesia.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...