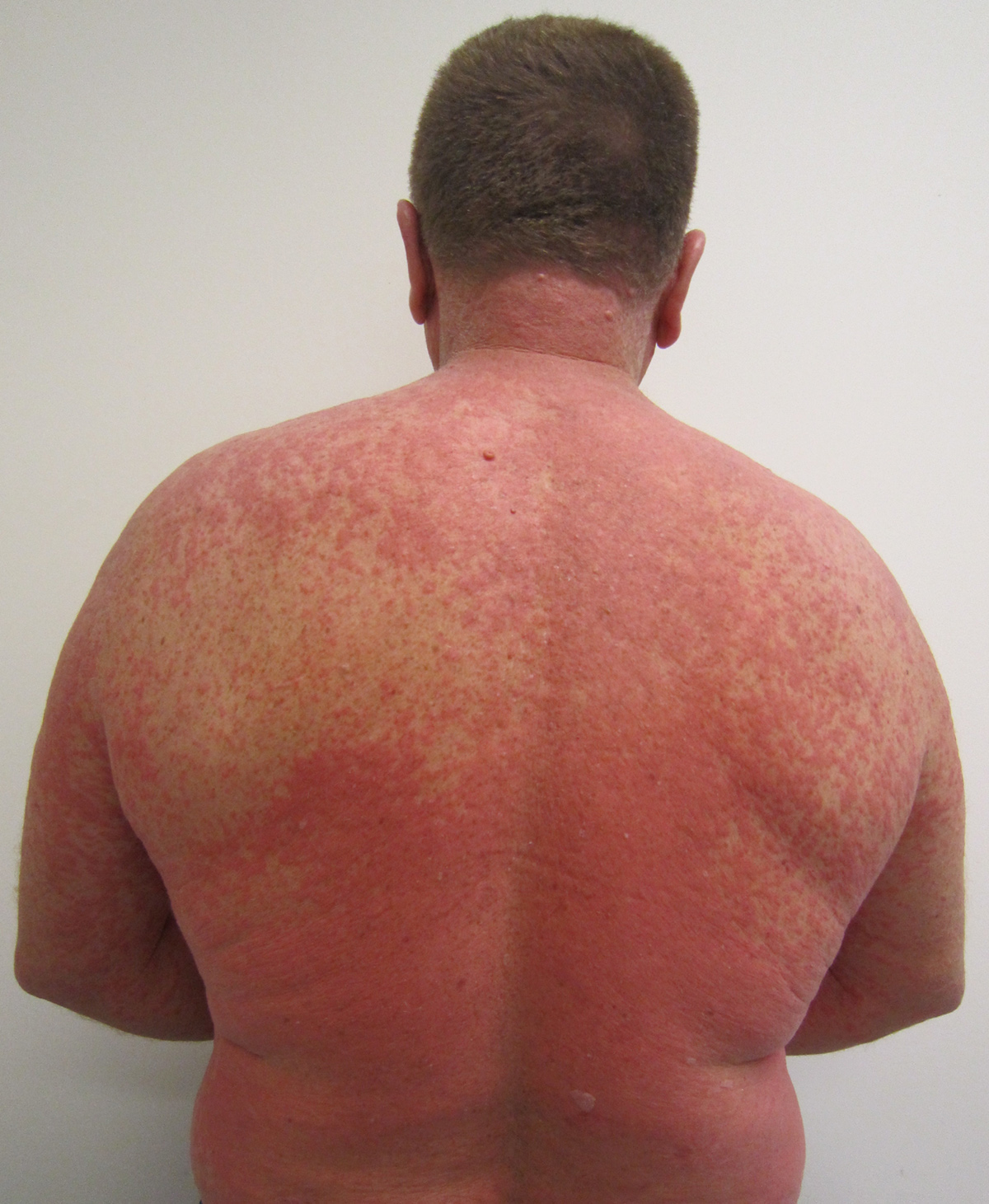
A drug allergy can occur with almost any drug, whether it is prescription or over-the-counter. This allergy occurs when a person’s immune system reacts to one or more components of a drug. It is possible to have a drug allergic reaction even if the same drug produced no adverse effects in the past.
Drug allergy should not be confused with side effects of a drug, which can occur to persons who are not allergic. Also, adverse reactions to a drug can be allergic and non-allergic. Either type of the reaction should be taken seriously because some effects can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of a drug allergy
In most cases, the allergic reaction starts immediately after taking the drug, or as soon as it is absorbed in the body. However, sometimes it may take hours or even days for the symptoms to start.
Typical symptoms of a drug allergy include skin rash, redness, hives, itching, mild or severe fever, swelling of the face, lips and tongue. They may also involve dizziness, difficulty breathing, confusion, fainting and anaphylactic shock. The last one is also considered to be a severe complication related to a drug allergy.
Complications of a drug allergy
Main complications that can result from a drug allergy include anaphylaxis, drug-induced anemia and serum sickness. Drug-induced anemia occurs because the reaction causes the immune system to start attacking and destroying healthy and normal blood cells.
Serum sickness can cause severe symptoms and potentially lead to organ failure. The general signs and symptoms of this condition include rash, fever and joint pain that start two to four weeks after a drug is first introduced.
Anaphylaxis is the most serious and most dangerous form of a drug allergic reaction. It is relatively rare but it can be fatal, especially if it is not treated immediately.
Anaphylaxis usually starts minutes after taking the drug. Drugs for topical use take longer to produce an adverse reaction. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include constriction or tightening of the airways, leading to severe difficulty breathing, shock, with weak and rapid pulse and very low blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bluish color of the lips and the nails, dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting.
This severe allergic reaction is always a medical emergency and if the patient is not treated on time it may result in death. It may require resuscitation measures, along with oxygen supplementation, intravenous fluids and airway management through a breathing tube.
The treatment primarily consists of epinephrine or adrenalin as soon as possible, given intramuscularly. People who are aware of existent allergies are advised to always carry an epinephrine autoinjector because this drug can save their life.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...