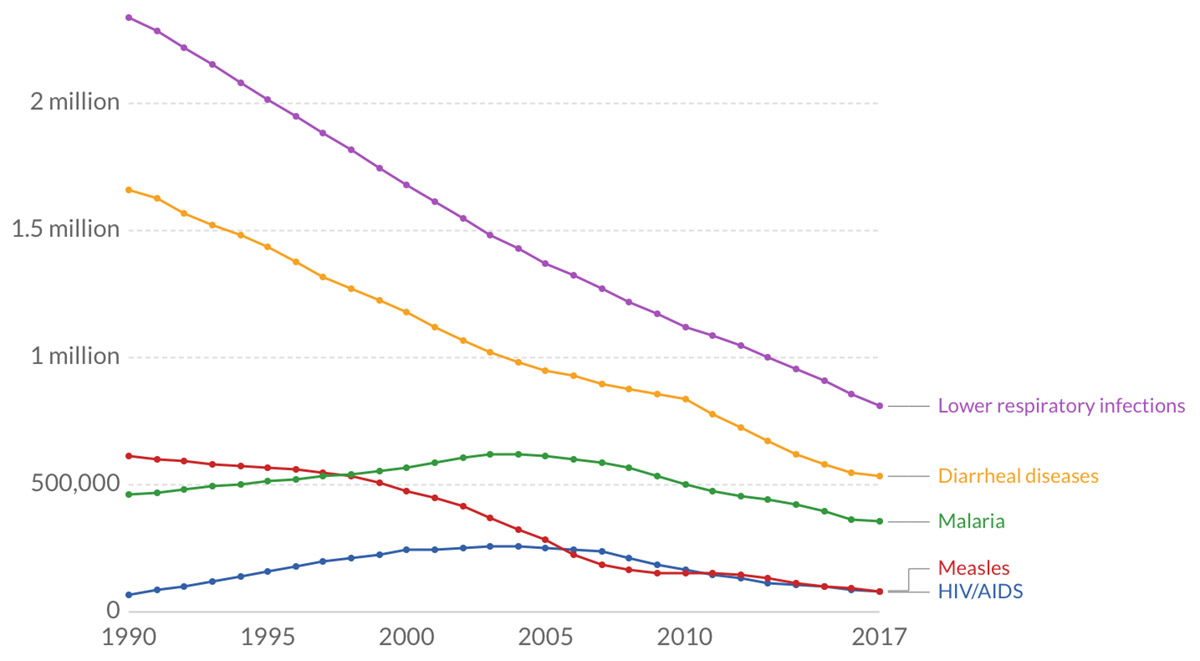
Infant Mortality Rate
Infant mortality rate is a number used to define the number of infant deaths per 1000 live births. Infants are babies who are no more than one year old. This rate is always given for a certain region, country or state and during the period of one year. The rate is calculated by dividing the number of dying newborns by the total number of live births during the year and multiplying it by 1,000. For numerous years, the leading cause of infant mortality everywhere around the world was dehydration from diarrhea. In recent years, this cause has been somewhat suppressed by spreading sufficient information about oral rehydration solution which consists of water mixed with sugar and salts. Nowadays, the leading cause of infant mortality is pneumonia, along with several other conditions which include SIDS, various types of infections, congenital malformation, malaria and malnutrition. Certain other less common causes of infant mortality include neglect, child abandonment, child abuse and in some cases even infanticide. There are also other subcategories of infant mortality and those include child mortality which includes deaths of children up to five years old, postneonatal mortality which includes deaths of infants between 28 days and one year old, neonatal mortality which includes deaths of infants no more than 28 days old and perinatal mortality which includes deaths between 22 weeks gestation and the end of the seventh day after delivery. The infant mortality rates have declined significantly as the Western civilizations grew bigger and more modern, mainly because of high technology used in medical advances and health care. It is important to stress out that the infant mortality rate is one of the most common standards of living evaluation in economics. Each country’s level of health and development is strongly correlated with its infant mortality rate. Areas affected by war also commonly experience a significant increase in their infant mortality rates simply because there are very strong external factors present, such as abuse and murder. War is also commonly associated with collapsed health care systems and difficulties in attaining basic medical care and supplies, especially when infants are concerned. Another big issue during a war is that all diseases which are otherwise preventable may easily rise to become epidemics. As a general rule, infant mortality rates are much higher in less developed countries than in more developed countries. The ratio is 17 to 1.
Infant Mortality Rates in Countries
The country with the highest infant mortality rate in the world is Angola and its rate is 180.21. It is closely followed by Sierra Leone which has an infant mortality rate of 154.43. The third on the list is Afghanistan with a rate of 151.95, and it is followed by Liberia with a rate of 138.24. On the fifth place is Niger with an infant mortality rate of 116.66. On the other hand, the country with the lowest mortality rate is Singapore with a rate of 2.31, followed by Bermuda with a rate of 2.46, Sweden with a rate of 2.71, Japan with a rate of 2.79 and Hong Kong with a rate of 2.92. The United States are characterized by an infant mortality rate of 6.3. Alabama has a rate of 8.96, Alaska has a rate of 6.45, Arizona has a rate of 6.69, Arkansas has a rate of 8.29, California has a rate of 5.22, Colorado has a rate of 6.27, Connecticut has a rate of 5.53, Delaware has a rate of 9.03, District of Columbia has a rate of 14.1, Florida has a rate of 7.24, Georgia has a rate of 8.35, Hawaii has a rate of 6.67, Idaho has a rate of 6.12, Illinois has a rate of 7.53, Indiana has a rate of 7.87, Iowa has a rate of 5.40, Kansas has a rate of 7.12, Kentucky has a rate of 6.79, Louisiana has a rate of 9.79, Maine has a rate of 5.87, Maryland has a rate of 8.00, Massachusetts has a rate of 4.89, Michigan has a rate of 8.02, Minnesota has a rate of 4.78, Mississippi has a rate of 10.74, Missouri has a rate of 7.63, Montana has a rate of 6.35, Nebraska has a rate of 5.89, Nevada has a rate of 5.86, New Hampshire has a rate of 5.05, New Jersey has a rate of 5.44, New Mexico has a rate of 6.13, New York has a rate of 6.02, North Carolina has a rate of 8.85, North Dakota has a rate of 6.35, Ohio has a rate of 7.82, Oklahoma has a rate of 7.86, Oregon has a rate of 5.68, Pennsylvania has a rate of 7.30, Rhode Island has a rate of 6.20, South Carolina has a rate of 9.03, South Dakota has a rate of 7.18, Tennessee has a rate of 8.87, Texas has a rate of 6.45, Utah has a rate of 4.92, Vermont has a rate of 5.37, Virginia has a rate of 7.50, Washington has a rate of 5.39, West Virginia has a rate of 8.1, Wisconsin has a rate of 6.34 and Wyoming has a rate of 6.95.
Infant Mortality as a Historical Economic Indicator
Infant mortality rate can also be observed as a rather important historical economic indicator because of the existence of a negative relationship between various economic factors, such as average wages, and the infant mortality rates.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...