Myopathy Definition
Myopathy is disease that has no cure. Treatments for myopathy are only to give patient a certain degree of relief. And it depends of the type, of a (congenital) myopathy. Some myopathy patients require hospital care and sometimes respiratory support. Some again may only need to work with a physical therapist or a different life style with the support of orthopedic bracing or surgery.
There are medications that only affect in order to aid and give the relief but can not treat latent diseases. Genetic therapy is advance therapy and may treat congenital myopathies by replacing or fixing defective genes. A stem cell therapy replaces faulty genes and creating the possibility to swap a faulty muscle cells with healthy cells.
- Muscles require a lot of energy to work properly, and metabolic diseases of muscle interfere with chemical reactions involved in drawing energy from food. When energy levels become too low, muscle weakness and exercise intolerance with muscle pain or cramps may occur.
- In a few metabolic muscle disorders, symptoms aren’t caused so much by a lack of energy, but rather by unused fuel molecules that build up inside muscle cells.
- Metabolic muscle diseases that have their onset in infancy tend to be the most severe, and some forms can be fatal. Those that begin in childhood or adulthood tend to be less severe, and changes in diet and lifestyle can benefit most people with the milder forms.
- MDA-supported researchers are pursuing a number of promising leads in their quest to understand the causes and discover treatments for metabolic diseases of muscle. One treatment strategy, called enzyme replacement therapy, already has led to the development of a successful commercial treatment for the metabolic disorder Pompe disease.
- Because rhabdomyolysis (acute muscle breakdown) is painful and can cause extensive kidney damage, many people with metabolic muscle diseases try to avoid triggering these episodes by modifying their physical activities. Each person must learn his or her activity limitations. Your MDA clinic director can help you work out a lifestyle plan to optimize your health and abilities.
- It’s unclear whether regular exercise is beneficial in the fat-metabolizing disorders, such as carnitine palmityl transferase deficiency. Because of their rarity, the characteristics of several of these diseases aren’t well known. A small percentage of adults with metabolic disorders may experience painful muscle cramps that have no obvious triggers; painkillers and meditation techniques may be effective under these circumstances.
- People with debrancher enzyme deficiency, carnitine deficiency and acid maltase deficiency may develop significant heart problems. If you’re at risk for cardiac problems, a cardiologist who’s familiar with your disorder should monitor your heart function.
- Some people with metabolic disorders have benefited from dietary changes. There’s evidence that those with carbohydrate-processing problems may be helped by a high-protein diet, while those with difficulty processing fats may do well on a diet high in carbohydrates and low in fat.
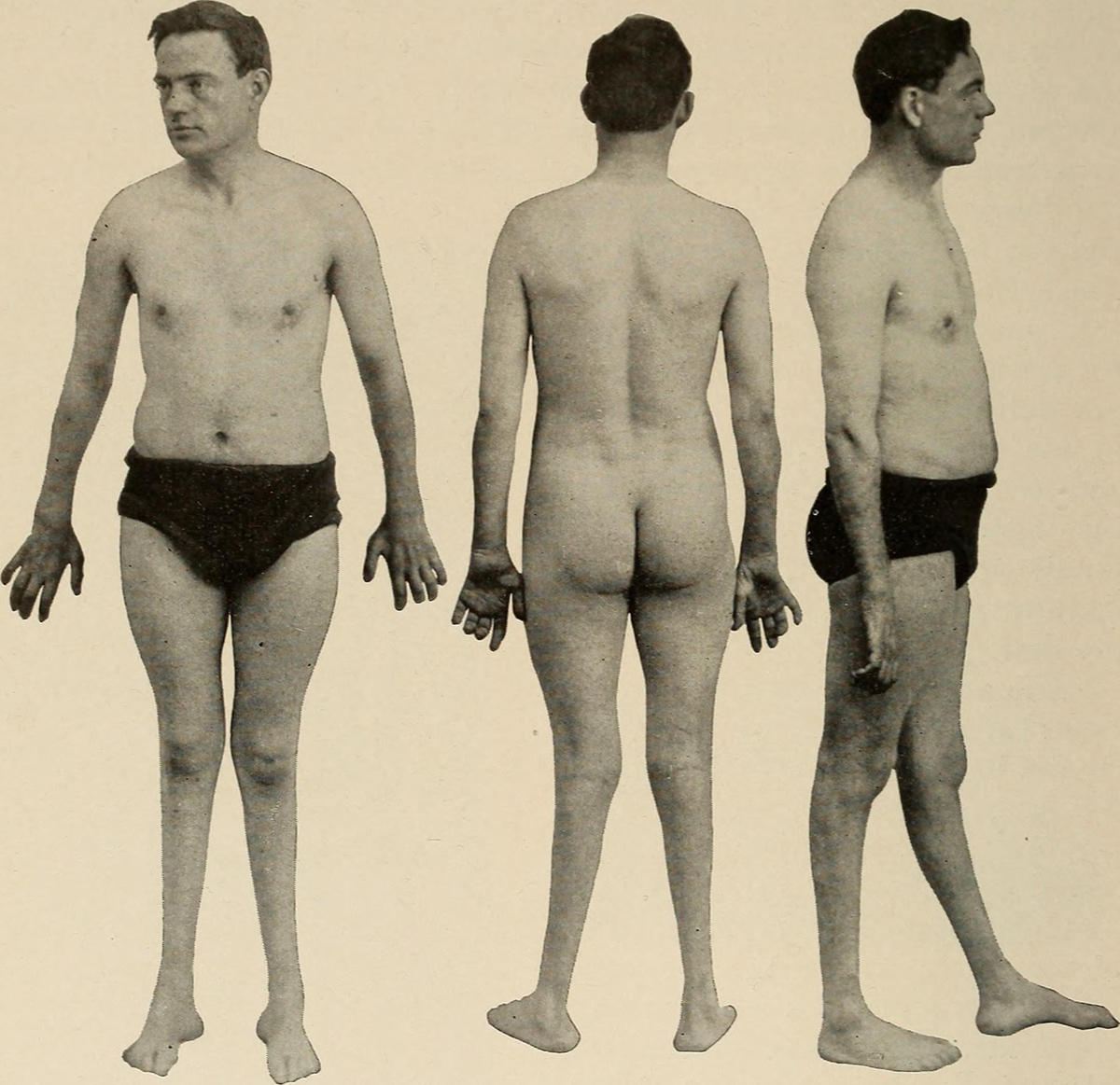
Types of Myopathy
Symptoms of Becker-type Myotonia or Myotonia Congenita or Thomsen's Disease are hard chewing or walking, muscle enlargement, postponed muscle stiffness or relaxation, and may occur in late childhood. Treatment includes exercises to relax muscles and suitable medications.
Symptoms of Eulenberg's disease or Paramyotonia Congenita occur at birth and include muscle weakness or muscle stiffness of face, neck, upper extremities. Stiffness can be provoked with cold or exercise and also weakness or paralyses that are caused by cold or exercise. If patient has no triggers medication may be the option.
Symptoms of Hyperkalemic Periodic Paralysis, which is basically a high potassium level in blood occur in childhood and are 15 minutes or day long general weakness a weakness after vigorous exercise and episodes that atrophy frequently with age and gets to be aggravated with stress or pregnancy episodes.
Symptoms of Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis or low potassium level in blood may appear in adult age or childhood and include almost paralysis severe weakness, weakness in the morning or at night, frequent symptoms from daily and lasts entire life. A proper dietary modification may limit hypokalemic periodic paralysis or hyperkalemic paralyses and no hard exercises. In this state induced medication may ease the condition.
Symptoms of Central Core Disease occur at birth and are non stop muscle weakness, bad muscle tone, inability to walk or postpone ability to walk with infants or skeletal deformities. Malignant hyperthermia and some anesthetic drugs may be fatal for central core disease patient so if there are surgery involved, it is important to check for anesthetic alternatives.
Symptoms of Nemaline Myopathy or Rod Body Disease occur at birth, childhood or in adult period and are heart problems, not speaking ability or swallowing disability, respiratory problems, weakness of the face, neck or upper limbs muscles, walking inability, a wheelchair necessity in the puberty and deformities of the skeleton because of the chronic weakness of muscles. Babies that suffer nemaline myopathy need a respiratory support and a feeding tube, and of course orthopedic and physical therapy to help out mobility of patient.
Symptoms of Centronuclear Myopathy or Myotubular Myopathy occur in childhood or birth and adult period. It is inherited disease and affects male children and it is called X-linked myotubular myopathy. The symptoms are not being able to walk, bad muscle weakness, respiratory difficulties, infections of the lung, liver abnormalities, anemia, gallstones etc. If patients have autosomal forms of Myotubular Myopathy, they have lighter muscle problems, but it gets worse with time. If new born has the X-linked myotubular myopathy baby won’t live too long. The autosomal forms of myotubular myopathy need monitoring or respiratory support and require physical or orthopedic therapies.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...