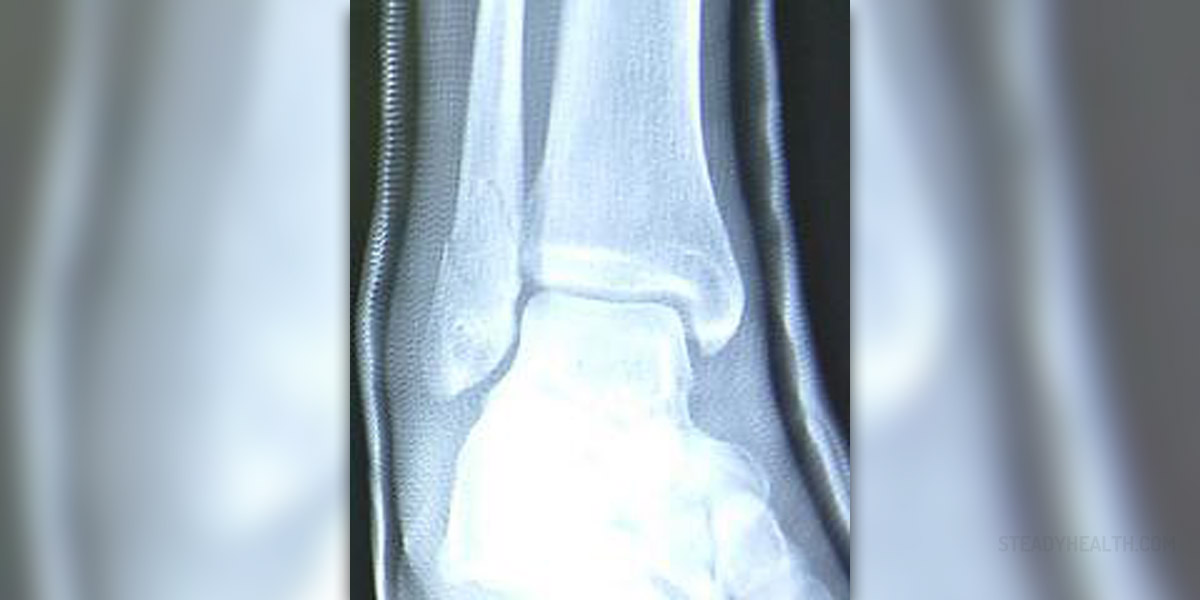
Almost every person knows that fibula is the bone which is present in the lower leg. Some people know fibula by the name of calf bone. Tibia is the thick bone which is palpable in the front portion of the lower leg and fibula is located on the lateral side of it. There are several long bones in the body and fibula is the thinnest and the most slender of them all. Even though tibia is a very strong and thick bone, there are a lot of fractures of it throughout the year. Not a lot of people know that when the tibia is fractured, fibula breaks as well because of the transmission of the force from the tibia. That means that when tibia breaks, fibula gets fractured as well.
Causes of Fibula Fracture
In most cases of fibula breaks, they are caused by a direct blow to the bone. Spiral fracture is more common in toddlers and small children. Spiral fractures occur due to the tortuous force acting on the fibula. Lots of people who participate in certain adventure sports suffer from fibula fractures a lot. Old people suffering from osteoporosis have a higher chance of breaking the fibula as well.
Treatment of Fibula Fracture
There are various factors which will determine the treatment plan for fibula fracture. The location of the fracture and its severity are the most important factors. Another important factor is whether tibia is involved or not. In most cases, the plan consists of a closed reduction and the placement of a cast. External fixation and even surgery are needed if the fracture is more severe. Bone grafting is possible as well.
The triangular shape of the fibula is dictated by the insertion points of the muscles on the shaft. The superficial peroneal nerve innervates the musculature of the lateral compartment and is responsible for eversion and, to a much milder degree, plantarflexion of the foot. Damage to this nerve may result in deficits in those movements. The superficial peroneal nerve also gives sensation to the dorsum of the foot.
- A truly isolated fracture of the fibula, one that has no other associated ligamentous or other bony injuries, are quite rare. They are typically the result of a direct injury to the leg, usually a fall or direct blow or blunt trauma like a sports injury or motor vehicle accident. Gunshot wounds are another mechanism from which an isolated fibula fracture can be sustained.
- While tibia fractures are most common in young males and elderly females, it is likely that most isolated fibula fractures are in the younger population, based on the injury responsible for these fractures. Young athletes, especially those involved in contact sports, and those individuals involved in motor vehicle accidents and pedestrian versus motor vehicle accidents, are likely at the highest risk.
- It is important to perform a thorough evaluation of isolated fibular shaft fractures to ensure they are, in fact, isolated. As in most orthopedic injury evaluations, it is good practice to check one joint above and below the injury. The knee should be checked for any ligamentous instability, and the ankle should be evaluated for any injury. Dedicated films of the knee and ankle are especially important to rule out other fractures in addition to lower-leg x rays. A fracture at the fibular neck without any other fractures in the rest of the fibula or tibia is pathognomonic for a syndesmotic injury and is termed a Maisonneuve fracture.
- In most instances, the treatment for isolated fibular shaft fractures is nonoperative. Since the shaft of the fibula is not a weight-bearing portion of the bone, patients can be treated with a weight-bearing as tolerated restriction, and some practitioners may utilize a walking boot for comfort.
- Patients with an isolated fibula shaft fracture typically have promising outcomes. These are often treated conservatively and symptomatically. There are seldom long term limitations, and patients often go on to union between 6-8 weeks if they have minimal comorbidities.
- Complications that are related to fractures of the fibula shaft are rare but do exist. Case reports exist of damage to the superficial peroneal nerve. There have also been reports of arterial damage and compartment syndrome in patients with isolated fibula fractures.
Fibula Fracture Healing Time
The time that is needed to pass in order for the fibula to heal properly is not the same with every person. There are various factors involved in this equation. The symptoms and the severity of the fracture will determine how much time it is needed to pass. Experts claim that fibula heals a lot quicker than most other fractures. In most cases, it takes between eight and ten weeks for the fibula to heal on its own. However, in most cases the muscles and the soft tissue will be sore after that period, so it may take up to 16 weeks for the fracture to be properly healed. A person will not be able to participate in any physical activity during the time while his or her leg is in a cast.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...