Electroshock therapy is a name once used for Electroconvulsive therapy. This therapy is used in psychiatric treatment to induce seizures electrically in anesthetized patients. What maybe comes as a surprise is that the exact mode of action of electroshock therapy still remains unknown. Despite that fact, electroshock therapy continues to be used in treatment of severe forms of different psychiatric conditions, such as depression. Usually, doctors recommend electroshock therapy when a patient doesn’t respond to any other form of treatment. The first electroshock therapy was completed in 1938, and it becomes widely used in mid 20th century.
How does it work?
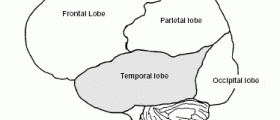
As already mentioned, the exact mechanism of action is still unknown. The reason behind this mystery is that there is no way to examine live human brain directly before and after the electroshock therapy. The goal of electroshock therapy is to induce therapeutic seizure that makes a patient lose consciousness and has convulsions. The seizure lasts for about quarter of a minute. Patient receives an anesthetic in arm and counts backwards until becomes unconscious. Doctors will put a rubber block into the patient’s mouth to prevent biting on the tongue. An oxygen mask is placed over the mouth to ensure optimum supply of oxygen to the brain. The patient wakes up in about half an hour, and usually feels very tired and exhausted. Patients will typically have six to twelve electroshock treatments over a week period.
Side effects of electroshock therapy
Electroshock therapy is associated with the same risks similar to brief general anesthesia. Patients usually feel confusion and memory loss, right after the treatment. Their muscles may feel very sore and they may suffer from a strong headache. The acute side effects also include amnesia that relates to the events occurring before the treatment as well as for those that happen after the treatment. In general, this is the worst side effect of this treatment, which is generally considered safe. Other common side effects include nausea and difficulty remembering newly learned information. In most cases, the memories will return. Moreover, certain patients have reported improved memory following the treatment, and removal of the amnesia that is often associated with severe depression. However this treatment may seem to be harsh, the amount of electricity that is used is much lower in intensity and duration than that which would be required to result in permanent brain damage. At this point, there is no evidence that electroshock therapy damages the brain, but it still remains one of the possibilities.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...