
Dwarfism or medically known as achondroplasia is basically a genetic condition. Affected adults do not grow higher than 147 centimeters . Their height basically ranges between 81 and 142 centimeters. The condition per se is not only associated with short stature. On contrary, these people face various challenges and are prone to deformities due to the abnormal development of their skeletal system.
Achondroplasia is definitely the most frequent cause of skeletal dysplasia. It is either inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion or develops as a consequence of spontaneous gene mutation on the chromosome 4, the one in charge of encoding fibroflast growth factors which regulate cartilage cell conversion.
Living a Life with Dwarfism Bone Disorder
The life of individuals suffering from dwarfism is rather challenging and full of various obstacles. The condition per se is stigmatized and most people have prejudice towards individuals with achondroplasia. As a result, they may no be well accepted by their peers or face difficulty when looking for a job. There is no mental retardation associated with dwarfism so there are no learning obstacles leaving these people an option to obtain higher education.
On the other hand, their skeletal abnormalities make them incapable of participating in certain activities and may eventually progress into more complex medical conditions.
From the very birth parents of babies suffering from dwarfism need to be in contact with the child's pediatrician who will supervise the baby's growth and development and provide with adequate advice regarding assistance on any kind. The pediatrician is also the one who can detect the onset of certain medical issues and recommend timely treatment.
Apart from at-home care, parents of children with disproportionate dwarfism should additionally pay attention to car seats, infant carriers and play equipment. Promotion of good posture is achieved with a footstool and a pillow for the lower portion of the spine. Some skeletal complications can be successfully prevented with a healthy diet and maintaining optimal weight. And finally, by encouraging the child to participate in certain sports such as swimming or bicycling parent will boost the child's self-esteem and make him/her feel a part of the society. Normally, doctors recommend the most convenient sports activities which do not contribute to further skeletal problems. For instance, people with dwarfism should abstain from gymnastics and contact sports.
Are Bones Prone to Injuries?
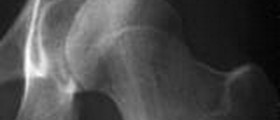
Degenerative hip disease is one of frequent issues associated with dwarfism. This problem is successfully dealt with total hip arthroplasty which is far better procedure compared to routine hip arthroplasty.
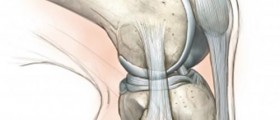
Each case of dwarfism is special because of its effects on the bones and joints. The effects of the gene abnormalities result in various deformities and specific degenerative changes. These typically reflect in limb deformities and deformities of the axial skeleton.
As for the age, most infants with dwarfism have to deal with thoracolumbar kyphosis and their knees joints show signs of extreme laxity. Toddlers suffer from a variety of bowleg deformities. And adults usually develop spinal stenosis and associated neurological issues. Osteoarthritis of the hip or knee joint are reserved for older age and practically never affect patients before they turn 40.
Basically, abnormal morphology of the affected joints is a reason why there is further tension load and an increase of weight-bearing forces on the particular body part. These individuals are additionally prone to secondary ligamentous laxity and associated problems. All the mentioned degenerative changes can be easily prevented if deformities are taken care of in early life. What is more, certain people suffering from dwarfism, usually the ones with asymmetry of the limbs require the accommodation of walking assists, reaching assists and beds as well as toilet facilities.
The deformities also depend on the type of the disease. For instance, in case of pseudoachroplastic dysplasia there is moderate scoliosis, severe ligamentous laxity and limb deformities along with hip luxation that basically affects toddlers.
Secondly, individuals affected by diastrophic dwarfism are prone to more complex musculoskeletal deformities including hip, knee and elbow deformities, mishappening of the hip joint and its luxation. Progressive spinal deformities occur as well.
Furthermore, in metaphyseal chondrodysplasia there is progressive bowling f the long bones. The hip deformity is in the form of coxa vara.
And finally, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita is a condition characterized by abnormal body proportion abnormalities, coxa vara and bowleg deformities.
In conclusion, it is clear that most of these deformities require timely treatment and correction. Surgery is in general the only treatment approach capable of providing with improvement of some skeletal abnormalities. These patients may, for instance, undergo total hip arthroplasy or a traditional femoral implant. Such surgeries do not differ from the ones performed in people who are not suffering from any kind of dwarfism.
All in all, the skeletal abnormalities are simply inevitable in people with dwarfism but with appropriate treatment severe complications and progression of the current symptoms can be successfully evaded.
Regarding life expectancy of people affected by achondroplasia, a type of dwarfism, babies and children under 2 years old have higher mortality, while those who reach adulthood in average reach age, slightly lower (approximately 10 years) than population that isn't affected by achondroplasia.




-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...