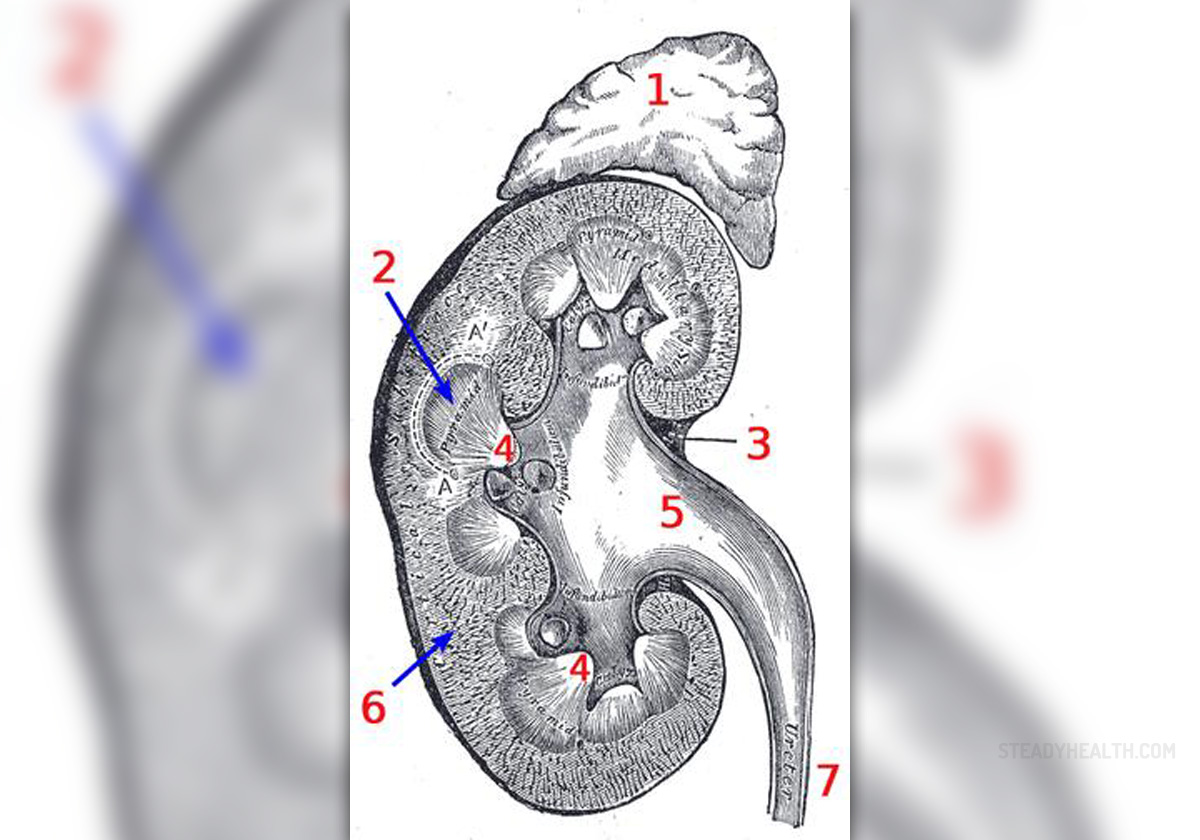
Severe kidney failure or end-stage liver disease can be treated with dialysis or kidney transplantation. Kidney transplantation is a more permanent solution because a new kidney completely replaces the function of the failed one. However, in certain cases kidney transplantation is not possible and dialysis is the only option.
Kidney transplantation
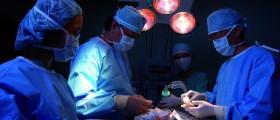
For many patients with renal disease kidney transplantation is the treatment of choice because it offers better prognosis and better quality of life compared to dialysis. One of the main problems with kidney transplantation is the shortage of organs available for patients. Candidates who fulfill certain conditions for transplantation are put on a waiting list and usually require dialysis until a kidney is available for them.
Because people can live and stay healthy with only one kidney, potential donors may include family members, if they are found to be a match for the patient. Kidneys may also come from a deceased person who was listed as an organ donor, but kidneys from living donors are considered better.
The conditions that prevent a person from being a candidate for kidney transplantation include old age, severe cardiovascular disease, active cancer, obesity, alcoholism, drug abuse, psychosis, inability to remember medications and severe chronic illnesses with negative prognosis. In most medical institutions, patients with HIV are not considered good candidates for transplantation, however, those patients may be eligible if their disease is well-controlled and in early stage.
Dialysis
There are two types of dialysis- hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. In hemodialysis, the blood is pumped through a machine that removes excess fluids and waste products from it. the patient is connected to the machine through a surgically created vascular access.
Hemodialysis can be done in a center or at home. In a center, it is usually done three times a week, for three to five hours per session. At home, it is done from three to seven times per week, for three to ten hours. Longer sessions can be done at night, while the patient is sleeping.
Peritoneal dialysis, which is usually done at home, uses fluid called dialysate that is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a catheter. Dialysate is left for a prescribed period of time, during which the peritoneal lining of the abdomen acts as a membrane that allows the waste and fluids to diffuse into the dialysate. After this, the dialysate containing waste and excess fluids is drained. Fresh dialysate is then introduced into the abdominal cavity and this process is called exchange. The exchange can be done manually or using a machine. Manual automatic can be done four or five times a day and automatic one is usually done during the night.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...