Oral surgical procedures such as extraction of the teeth or minor oral interventions carry a small risk of complications. These include mainly hemorrhage, pain and infection. But if one follows the prescribed regimes and keeps the oral hygiene properly complications may be reduced and their intensity decreased.
Usual Complications Following Oral Surgery
The most common complication or better to say side effect of oral surgery is bleeding. It may eventually stop but in order to speed the process, one can firmly pressure the bleeding spot with gauze. It is recommendable to keep the gauze pressed for at least 20 minutes. This complication may occur if a patient brushes the teeth vigorously or use mouthwashes after the surgery.
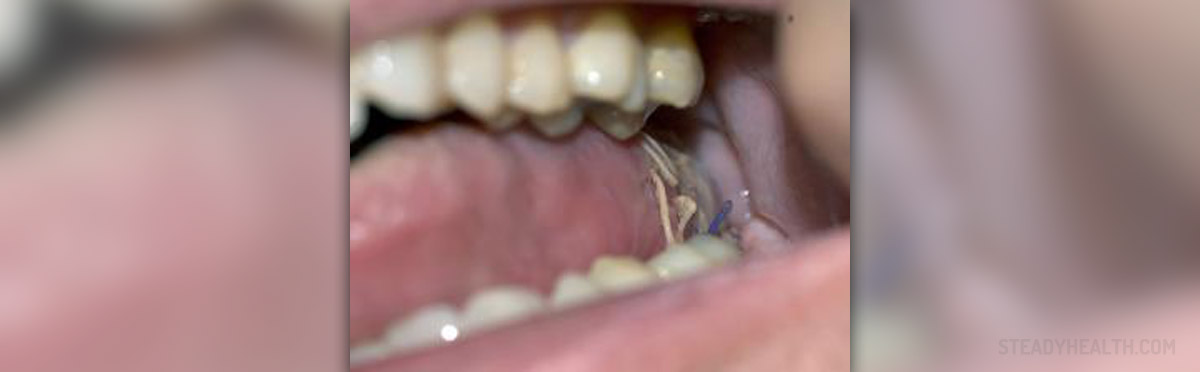
Infection occurs in rare cases since patients at risk are prescribed antibiotics as a form of prophylaxis. Infections are followed by high temperatures. Pain is normally present. The painkillers are regularly prescribed. The pain is considered as something generally present after each and every operation. In the case of oral surgery, pain is considered a complication if it lasts longer than two weeks after the sugary. This may point to the presence of a blood clot in the tooth socket. In that case, the patient is due to report this to his dental surgeon who will take care of the problem.
Swelling develops as a result of fluid extravasation into the tissue which surrounds the wound. The second and the third days feature the largest swelling. Cold compresses held on the area may reduce the swelling and the body position in which the head is above the heart (sitting, semi-lying) may be helpful as well. Mouth bruising is present together with the swelling. The muscles of the jaw may be stiffed for a week or two hence they make chewing and swallowing difficult. The last complication is not so common.
Rare and Serious Complications
In case of tooth extraction tiny parts of the extracted tooth may remain in the gum. These are responsible for prolonged pain, and may even lead to bleeding while eating. In case they do not eliminate themselves the patient is due to visit his/ her dentist to have them removed.
Delayed healing process is caused either by one or more complications joined together. They lead to difficulties with eating and nervousness. These secondary complications are minor and one should not worry about them. The food can always be prepared in a form of mash, fruit made into juice, and vitamins and minerals are taken in a form of supplements.
Serious post-dental complications are rather rare and they include extremely high temperature, worsening of the pain and swelling, puss collections and excessive or prolonged bleeding.
- This study reviewed the records of 324 patients (171 males, 153 females; with a mean age of 41.0 years, ranging from 5 to 84 years) who underwent surgical treatment in the operating room under general anesthesia or intravenous sedation at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery, Hiroshima University Hospital, from 2012 and 2014.
- A total of 36 cases had postoperative complications (overall rate of 11.1%), of which four showed surgical site infection and 32 an anastomotic leak without a distinct infection sign.
- Albumin level, in particular, is thought to be a reliable marker of nutritional status in patients following surgery, with a decreased level associated with rheumatoid disease, indicating it as a promising marker of inflammatory disease.
- In addition, serum albumin is thought to be a predictive nutritional parameter for patients with head and neck cancer. In a previous study, preoperative albumin level in serum was identified as significant risk factor for surgical site infection in those who underwent primary resection, and head and neck reconstructive surgery.
- Postoperative oral hygiene is considered necessary for patients who have difficulty with oral cleaning due to surgical damage, as microflora harbored in the oral cavity may be composed of pathogens related to surgical site infection. Recently, oral health care has become recognized as essential to decrease postoperative complications in head and neck cancer, as well as other patients with cancer.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...