What is Hypocalcemia?
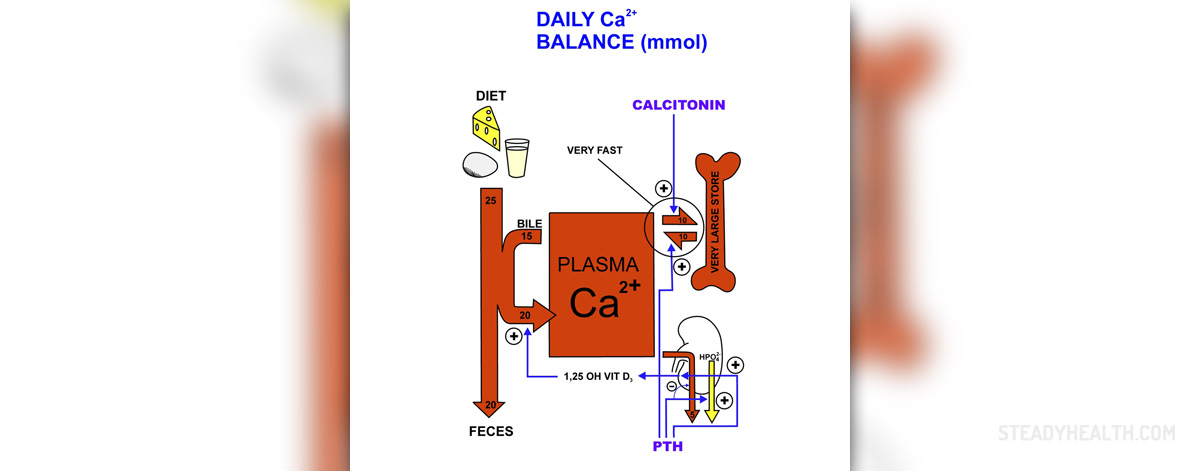
Calcium deficiency or hypocalcemia is marked by low calcium blood level in which ionized calcium level in the blood is lower than 4.0 mg/dL. Normal value of serum calcium levels in the blood is 4.0-6.0 mg/dL.
Causes of Hypocalcemia
A low calcium level in the blood can result out of hypoparathyroidism in which the parathyroid gland fails to produce parathyroid hormone. This hormone regulates plasma calcium levels therefore its deficiency leads to low blood calcium levels.
Kidney failure can also lead to hypocalcemia. The kidneys synthesize 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D that stimulates absorption of calcium from the diet and the mobilization of calcium from the bones. The synthesis of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D is triggered by the effect of parathyroid hormone but in case of kidney failure this process is ineffective resulting in low levels of calcium in the blood.
Hypomagnesemia or magnesium deficiency can be also responsible for hypocalcemia. Low levels of magnesium in the blood affect the activity of parathyroid hormone leading to low blood calcium levels. Hypomagnesemia is associated with alcoholism and disorders featured by failure to absorb fat. Thereby, any disease that lowers plasma magnesium levels can cause hypocalcemia.
Intake of toxic levels of phosphate can also lead to hypocalcemia. This may take place if people ingest enema formulas that contain phosphate which are used for cleansing of the intestines. It can also occur if an enema is administered to infants or if infants are fed with phosphate-rich formula.
Symptoms of Hypocalcemia
Mild hypocalcemia usually does not cause symptoms. However, over time when blood calcium levels become extremely low the symptoms start to appear. Common symptoms of hypocalcemia is neuromuscular irritability featured my muscle spasms and twitching. Mucsle spasms usually occur in the face, feet and hands. Tingling in the mouth, feet and hands often accompanies hypocalcemia. Depression, hallucinations, confusion and memory loss are other symptoms of calcium deficiency. Chornic hypocalcemia is associated with cataract.
Diagnosis of Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia can be diagnosed by routine blood test. It is done by analysis of blood sample, which involves measuring of free calcium level with the help of calcium-sensitive electrode. Since hypocalcemia can result out of many different conditions, it is necessary to make assessment of kidney function and parathyroid gland as well as to measure blood levels of parathyroid hormone, magnesium, phosphate and vitamin D.
Treatment of HypocalcemiaHypocalcemia can be treated with oral calcium supplementation or intravenous administration of calcium. Vitamin D supplements are also used in treatment of calcium deficiency as this vitamin helps absorption of calcium.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...