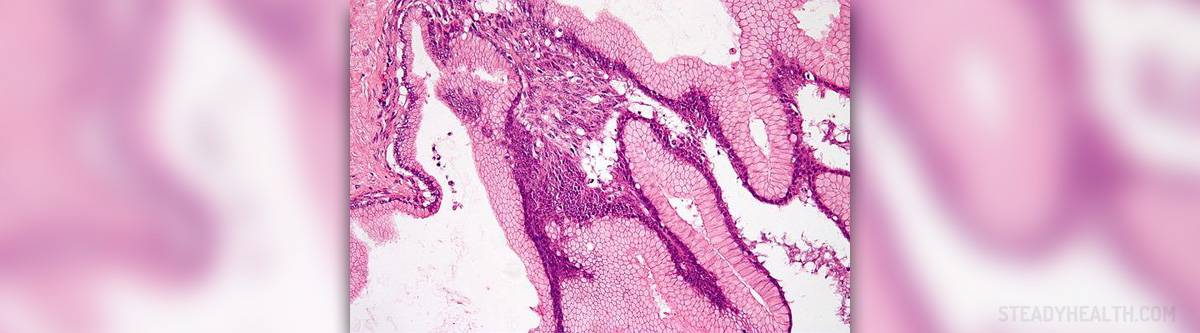
Ovarian cystadenoma is a benign tumor that affects the ovary and develops in a form of a cyst (hence the name). A cystadenoma is not an actual cyst. It is a cystic tumor which may grow larger than a simple cyst and often requires surgical removal.
The tumor occurs as a consequence of abnormal growth of certain ovarian cells. To be more precise, it originates from ovarian cells. Fortunately, the tumor is benign. Still, if it gets large enough it can cause serious problems.Types of Ovarian Cystadenoma
There are two types of ovarian cystadenoma. Serous cystadenoma is a typical benign tumor of the ovary which occurs in a form of a cyst filled with watery liquid. Mucinous cystadenoma, on the other hand, comprises sticky, thick liquid. Serous cystadenomas may grow up to 6 inches in diameter while mucinous cystadenomas grow even bigger reaching 12 inches in diameter. It may sound amazing but there were cases when the tumor weighted up to 100 pounds.
Serous ovarian cystadenoma is considered rather common tumor. Its superficial appearance may lead a doctor to suspect serous carcinoma of the ovary while performing microscopic evaluation. However, a well-experienced doctor will know the difference.
Diagnosis
Small cystadenomas are asymptomatic and can be easily found during regular gynecological ultrasound examination. What follows is checking for the presence of liquid inside the cyst. The doctor also investigates whether the tumor is cystic or solid.
Definitive confirmation is archived after pathohistological examination of the tumor once it is surgically removed. The tumor comprises unilocular cyst and is filled with clear and straw-colored liquid.Treatment for Ovarian Cystadenoma
The only way to deal with ovarian cystadenoma, no matter whether the tumor is serous or mucinous, is surgical removal. It is essential to pay close attention and remove the tumor in toto, never allow the cysts to burst and spill the content of the tumor inside the abdominal cavity.
Small cystadenomas are easily removed laparoscopically. This way the surgeon makes a small cut in the abdomen and inserts a narrow tube (a laparoscope) which allows inspection of the abdominal cavity and removal of the tumor.
Cystadenomas larger than 2 ½ inches in diameter require open surgery. In some cases the doctor will have to remove the ovary together with the tumor.
Fortunately, once the tumor is removed it generally does not reoccur. Even if one ovary is sacrificed, the woman is left with the second ovary and may be able to conceive a child.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...