Antibiotics are medications that are prescribed to treat infections and conditions caused by different types of bacteria. These medications are widely used and before they were invented many people have died from illnesses that are today common and easily treated.
However, the use of antibiotics carries certain risks. One of them is that inappropriate use of antibiotics can lead to resistance of the bacteria which do not respond to the treatment anymore and overgrow instead. The other major concern regarding antibiotics is allergy.
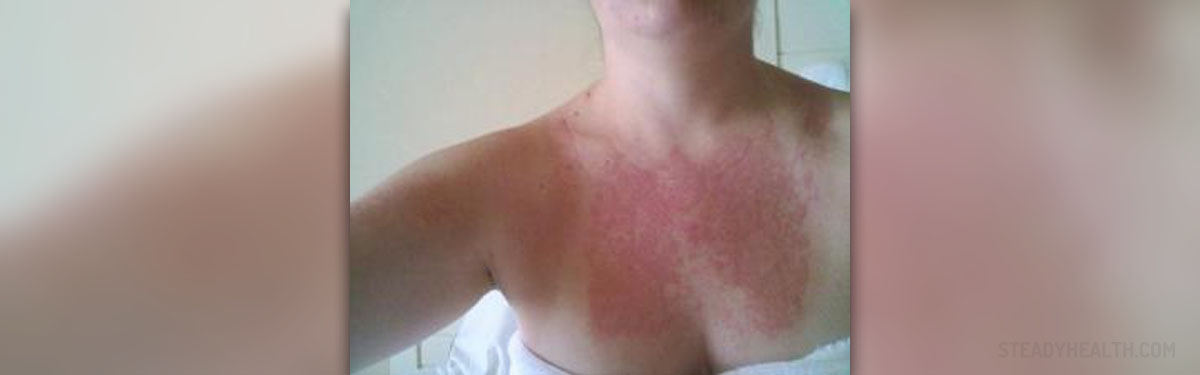
Some people are aware of their allergy to certain antibiotics and they usually take other types of antibiotics instead. However, a new allergy can occur at any point, which is why it is important to know the signs of an allergic reaction to antibiotics and to take steps to treat it.
Some of the antibiotics that can cause allergies in both adults and children are amoxicillin, ampicillin, penicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, Ciprofloxacin, and vancomycin.
- Antibiotic allergy has a strong impact on the development of health-care associated infections and antibiotic resistance. For instance, inpatients with penicillin allergy have a significantly higher frequency of infections by several agents, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus species and Escherichia coli. In patients with a history of penicillin allergy the risk of adverse events triples because they receive alternative antibiotics which often have a greater risk of side effects. Hospitalizations of patients with a history of penicillin allergy have a longer average length of stay and higher hospital charges in comparing with patients without penicillin allergy in the past.
- Antibiotic hypersensitivity is a common reason for visits and admissions to hospitals. According to different studies, up to 12% of all visits to emergency departments are due to different adverse drug events, including antibiotic allergy. In the United States, antibiotics are implicated in 13.7% of all adult emergency department visits. Allergic reactions account for approximately 74% of these visits. Anaphylactic shock, angioedema and urticaria which lead to hospitalization in Poland, the most frequently occurs after taking antibiotics. In Italy, the main cause of emergency departments visits and hospital admissions caused by drugs was antibiotic hypersensitivity. In the United Kingdom, increasing of cases of iatrogenic anaphylaxis which lead to hospitalizations is associated with increased antibiotic prescriptions.
- A total of 5176 patients (1759, 1864 and 1553 patients in 2015, 2016 and 2017 respectively) were admitted to the Unit during this study period. Antibiotic hypersensitivity reactions were noted as the reason for hospitalization in 101 medical records (37, 36 and 28 patients in 2015, 2016 and 2017 respectively). The incidence of antibiotic allergies was almost 2.0% (95%CI 1.6:2.4) of all admissions to the Unit during study period with tendency towards to not statistically significant decreasing: 2.1% (95%CI 1.5:2.9) in 2015, 1.9% (95%CI 1.3:2.6) in 2016 and 1.8% (95%CI 1.2:2.6) in 2017 (p>0.05).
- The admissions included 79 (78.2%; 95%CI 68.9:85.8) females and 22 (21.8%; 95%CI 14.2:31.1) males. The female predominance was established for each year of study period (p>0.05). The mean age of patients was 48.5 years (SD=17.0; range 18-83 years). The length of hospitalization varied from 2 to 13 days, a mean of 8.2 days per patient (SD=2.2). During research period each of our sample used a mean of 5.4 medicines (SD=1.2), from 3 to 12 items. The total number of prescribed drugs was 541. There was no statistical significance in the distribution of all above items in 2015, 2016 and 2017 (p>0.05).
- Antibiotic allergic reactions in 37 (36.6%; 95%CI 27.8:46.8) cases were manifested as urticaria, 11 (10.9%; 95%CI 5.6:18.7) - as angioedema and 53 (52.5%; 95%CI 42.3:62.5) - as urticaria with angioedema. Moderate to severe health status of patients on admission were noted in 97% (95%CI 91.6:99.4) of the medical records. About 36% (95%CI 26.4:45.8) of patients had allergic reactions in the past to different drugs, but names of drugs were noted only in 44.4% of medical records.
Symptoms of Antibiotic Allergy
The symptoms that occur as a result of an allergic reaction to antibiotics can vary from mild to severe. Severe reaction or shock is possibly life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Allergic reactions depend on the type and the quantity of the antibiotic taken. A reaction starts within 24 hours after taking the medicine and after taking appropriate measures it stops after a few hours.
Rash or hives are one of the common signs of allergy. They usually appear around the mouth and the neck first and they can extend to other parts of the body. Redness, swelling, and itching, as well as pain and tenderness of the rash, are possible.
A very serious and severe form of allergic reaction is called anaphylactic shock. It is characterized by the inability to breathe due to swelling followed by wheezing, coughing, and choking, with other symptoms like low blood pressure, weakness, pale skin, blue lips, and fainting.
Treatment for Antibiotic Allergy
The first step is to discontinue the antibiotic and seek medical care. Rash and hives are usually treated with corticosteroids and antihistamines. Treatment duration depends on the severity of the allergy, and after all the signs of the reaction are gone, the patient is advised to avoid that particular antibiotic in the future.
Anaphylactic shock, which requires an immediate response, otherwise it may have a fatal outcome, is commonly treated with injectable epinephrine or adrenaline. This treatment has no side effects and it works fast. It improves the airflow almost immediately and regulates the drop in blood pressure. The patient may also be given intravenous fluids due to fluid loss that often accompanies anaphylaxis.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...