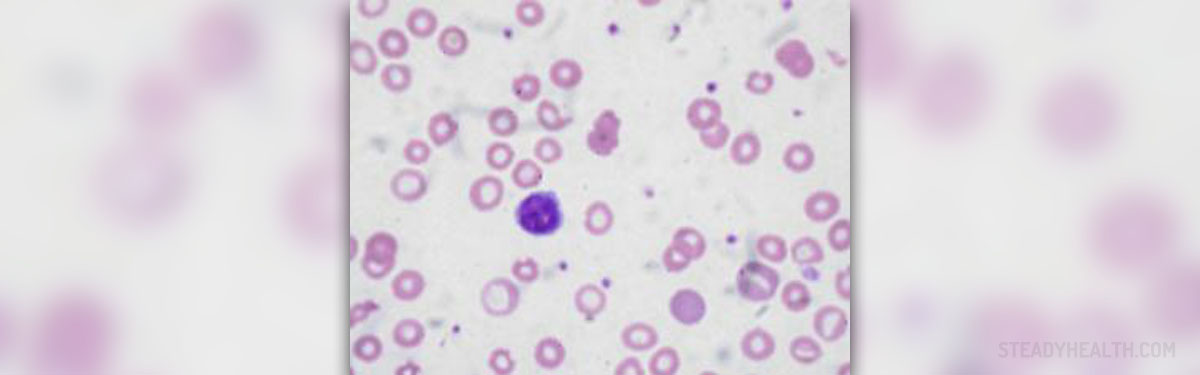
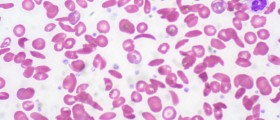
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a decrease in a number of red blood cells, or low levels of hemoglobin in the body. Hemoglobin is a key constituent of red blood cells, and plays a very important role in human health since it possesses a unique oxygen-binding ability, which makes it capable of attaching the oxygen molecule from the lungs and carrying it away throughout the body to feed every living cell. If a person lacks in an optimum number of red blood cells or has abnormally low levels of hemoglobin in the body, all of the organs in the system will suffer, since they become deprived from oxygen. All of the cells are very dependent on oxygen for survival and different levels of anemia may result in different serious medical conditions. However, anemia can only be temporary in some cases, but it can also be long term, and more serious. In the same manner, anemia ranges from mild to severe.
Symptoms of anemia
Signs and symptoms of anemia can be different in various people. The exact nature of anemia depends on what causes it. In most of the cases, anemia remains undetected, especially if it is mild. However, signs and symptoms of the disease are typically becoming more severe as the disease progresses and affect the living tissues. Among the most prominent signs of anemia are very pale skin, extreme fatigue, shortness of breath (especially after the light physical effort), fast or irregular heartbeats, dizziness and vertigo, angina or chest pain, cold hands and feet, persistent headaches and noticeable cognitive problems. Chronic anemia is especially dangerous in children since it may result in behavioral disturbances and reduced school performance. Other symptoms include low blood pressure, yellowing of the eyes, enlargement of the spleen and changes in stool color.
Causes of anemia
Anemia occurs whenever the blood does not have enough of red blood cells. This occurs either if the body does not make enough red blood cells, or because it destroys the red blood cells, for some reason. Anemia can also occur whenever the bleeding causes excessive loss of red blood cells, and the body is unable to replace them on time. In most of the cases, anemia occurs as a result of iron deficiency. This nutrient is essential for bone marrow to make hemoglobin. In the same way, vitamin deficiency, especially of folate and B-12, causes anemia. In some patients, anemia results from a chronic disease such as HIV, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis or any type of inflammation. It is also a very common side effect of different bone marrow diseases.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...