Dopamine or DA, as it is sometimes abbreviated, is a neurotransmitter. Its chemical name is 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol and it works by affecting several dopamine receptors, named D1, D2, D3, D4 and D5 and variants of these receptors. This neurotransmitter is produced in the brain, especially in the areas known as the ventral tegmental and substantia nigra. Hypothalamus can also produce this neurohormone.
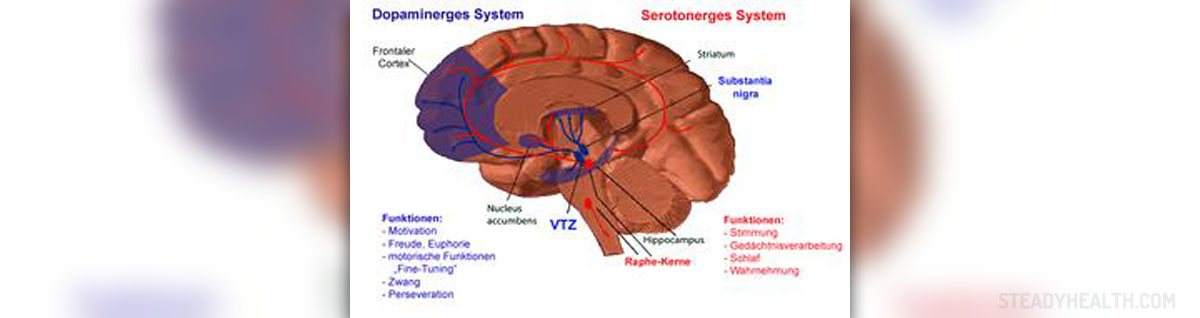
Dopaminergic Pathways
Dopaminergic neurons transmit dopamine from one to another part of the brain and we know about 4 major dopaminergic pathways. There are mesolimbic, mesocortical, nigrostriatal and tuberoinfundibular pathways of dopaminergic neurons.
The mesolimbic pathway transmits dopamine form the midbrain, ventral tegmental area (VTA) to certain nucleus (n.accumbens) located in the limbic system. The mesocortical pathway transmits dopamine from VTA to frontal cortex. The nigrostriatal pathway transmits dopamine from the substantia nigra to striatum. Patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease usually experience problems with functioning of this dopaminergic pathway. And finally, the tuberoinfundibular pathway transmits DA from hypothalamus to the pituitary gland and affects secretion of different hormones.
Functions of Dopamine
Dopamine has numerous functions in the human body. It affects our behavior and cognition as well as our motivation and reward. Our voluntary movements are also under the influence of DA. Human sleep, mood, attention and learning are also affected by dopamine. This hormone can inhibit production of prolactin, via the tuberoinfundibular pathway. Every time we try to learn something, dopamine gives certain signals to the part of the brain responsible for learning new behavior.
Dopamine controls the flow of information to the frontal lobe from all other areas of the brain. If a person suffers from some dopamine disorder, this may result in memory and attention issues and difficulties to solve some problems. ADD (attention deficit disorder) is also believed to be associates with decreased concentration of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex of the brain.
Dopamine is also responsible for learning and seeking reward. This hormone is additionally involved in signaling when there is something wrong with prediction of reward, cognition and motivation, so addiction, consumption and approach are behaviors associated with dopamine. Dopamine neurons seem to fire increasingly especially if the given reward is more than it was expected.
DA is included in motivation and pleasure and every time we feel good, there is some dopamine released in our brain. It might be our favorite food or drink, something nice we feel, sexual activity or anything else we enjoy doing and it will provoke release of this hormone. Nicotine, amphetamine and cocaine are believed to increase the amount of this hormone released in the brain.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/schizophrenia/causes/
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/psychosis/causes/
- Photo courtesy of INeverCry by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dopaminsystem.png
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...