
Foods rich in calcium are an important part of your daily diet, with the World Health Organization recommending that people get at least 500 mg a day — though the exact recommendation depends on your sex and age, as well as whether you might be suffering from certain medical conditions that require a higher intake of this mineral.
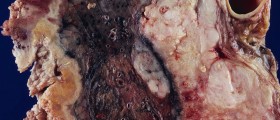
This mineral normally does not accumulate in any of the organs within the body, so if this occurs, it points to the presence of an underlying medical condition. The pathological accumulation of calcium may affect the lungs, heart joints, bones, and even skin.
Causes of Calcium Deposits in Lungs
The condition in which calcium accumulates in lung tissue is known as lung calcification, while calcium growths that appear inside the lungs are known as a pulmonary granuloma.
Lung calcification may occur in patients suffering from chronic lung infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Furthermore, exposure to asbestos increases the risk of lung calcification.
Increased accumulation of calcium in the lungs may also happen due to excessive levels of vitamin D. This "sunshine vitamin" is in charge of the absorption of calcium.
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection of the lungs. It leads to scarring and scars are excellent places for calcium deposits to form. Lung calcification also occurs in certain patients suffering from tuberculosis. Even certain cancers may increase the risk of accumulation of calcium in the lungs.
Symptoms of Calcium Deposits in Lungs
Some patients may experience different symptoms which lead them to seeing a doctor or multiple doctors, who eventually discover the presence of calcium deposits in the lungs. The symptoms are going to be closely based on the underlying condition ultimately responsible for the calcification, and this is why the symptoms of calcium deposits in the lungs are not the same in all patients suffering from lung calcification.
Diagnosis of and Treatment for Calcium Deposits in the Lungs
Calcium deposits in the lungs are most commonly detected accidentally, during examinations that are performed for other, unrelated, purposes or because the patient reports symptoms that cause doctors to order general lung exams.
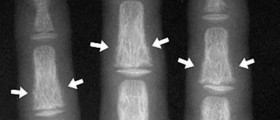
Many people do not even know they have deposits of calcium in their lungs until symptoms become clear and troublesome. Lung calcification can be easily noticed on a chest X-ray. Better insight into the scope of any calcium deposits is achieved through performing a CT scan of the lungs. Once the doctor has found calcium deposits in a patient's lungs, he or she continues with examinations and tests to determine the underlying cause of the disease.
In the majority of cases of lung calcification, the goal of the treatment is to alleviate the symptoms of the underlying condition responsible, and perhaps symptoms of the very calcium deposits. Once calcium has accumulated in the lungs, it simply cannot be removed. But doctors will do their best to prevent further accumulation of calcium and possible complications.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/sarcoidosis/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000175.htm
- Photo courtesy of Fru00e9du00e9ric BISSON by Flickr: www.flickr.com/photos/zigazou76/4850035359/













Your thoughts on this
Loading...