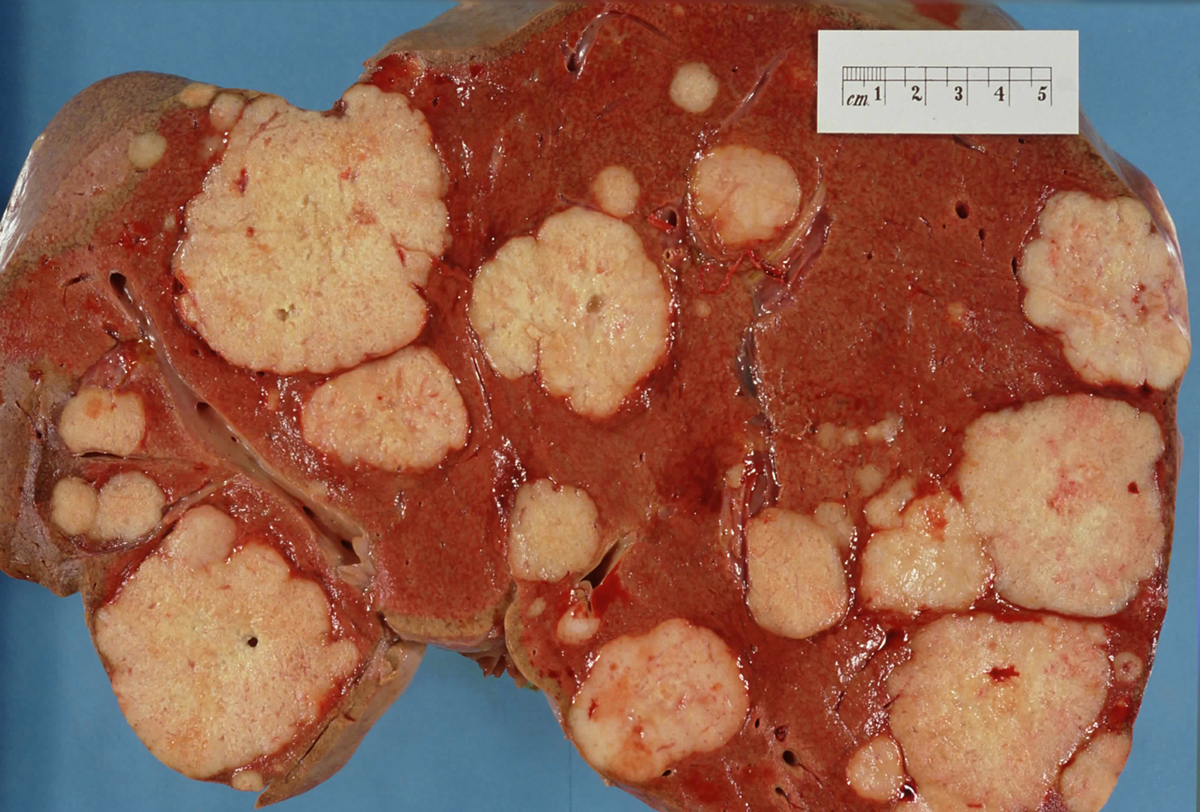
Secondary Liver Cancer
Every cancer has the ability to spread in different ways. It can directly affect and infiltrate the surrounding tissue or is can spread through lymphatic or blood vessels. Secondary liver cancer is in fact a deposit of cancer cells originating from the primary cancers that are situated in distant organs. Secondary liver cancer is therefore a metastasis of the primary cancer which can affect every organ in the body. Even in patients who have liver metastases a surgery can be possible and is performed in certain cases. Colorectal cancers are prone to give liver metastases. In this case the surgery of the liver is performed only if the cancer cells have affected limited area of the liver and if there is no evidence of cancer spreading to other tissues and organs. However, if other organs are affected by tumor cells as well the patient will not be operated. Instead he/ she will be given chemotherapy.
Prior the surgery a doctor needs to be sure that there are no deposits of cancer cells in other parts of the body so the patient will have to undergo certain examinations such as ultrasonography, CT scan and MRI of certain body areas. In case of colorectal cancer even testing for tumor markers can be of additional help. Surgery for Secondary Liver Cancer
In case of secondary liver cancer, a surgeon performs resection of the metastases. This operation lasts approximately between 3 and 7 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. A patient should not worry about the loss of liver function since this organ can perfectly regenerate and the resected part will grow back within several months. The resected liver will continue with its function properly. Prior the very surgery a patient may be administered chemotherapeutics which will assist in reduction of the tumor and make the operation less extensive. Chemotherapeutics may be also administered after the surgery.
Unfortunately, liver transplantation is not a surgical option for people suffering from secondary liver cancer. They are not suitable candidates because the tumor can reoccur within certain period of time.
Portal vein embolisation includes insertion of the tube into a vein of the liver part that is going to be resected. This can in some cases enhance the enlargement of the healthy part of the liver.
After the Surgery
Because of the potential risk of postoperative bleeding a patient is monitored for 24 hours in intensive unit care after the surgery. After that he/ she is kept in hospital for a couple of weeks and then discharged. In the beginning the patient will be administered intravenous fluids, but only for a few days. Restricted diet is advised in the beginning but once the patient has recovered he/ she may continue with every day diet. The pain after liver surgery is brought under control by certain painkillers.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...