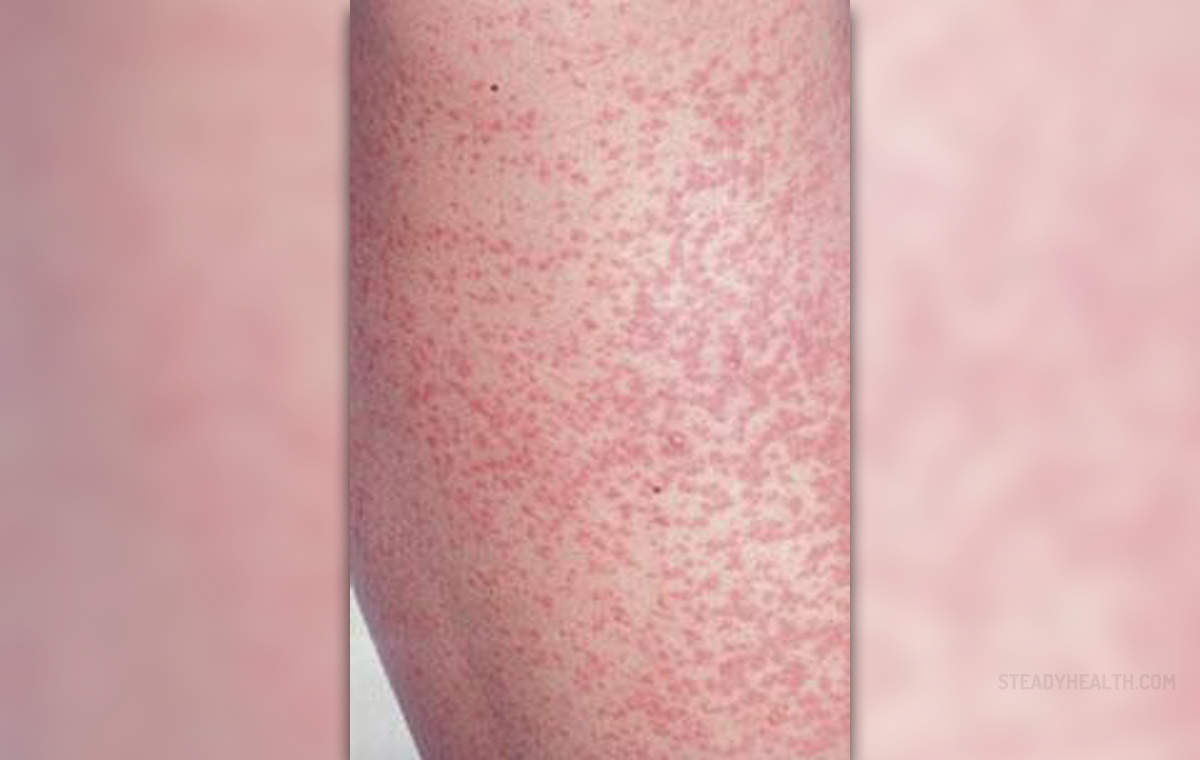
There are not that many people in the world who have never heard of rubella. Some may know this condition as German measles as well. The data shows that this disease is not that common as it used to be since the introduction of routine childhood rubella vaccination. Ever since that was the case, there were less and less cases of rubella in North America. However, rubella can occur during pregnancy as well and if that happens, the unborn child will be in real danger.
Definition of congenital rubella syndrome
Even nowadays, with the available vaccine, there are still cases of rubella. If this infection occurs in women who are not pregnant, there is no need for worry because such an infection has no great impact on the health of a woman and the disease itself is self-limited, in most cases characterized by a rash. A woman will be infectious for a period of one week before the rash occurred and up to 7 days after the rash. Women need to know that in almost 50% of all rubella cases, the infection is asymptomatic but there are some women who may experience some other symptoms as well like low-grade fever, conjunctivitis, sore throat, coryza, headaches and even sensitive lymphadenopathy. In almost all cases where these prodromal symptoms are present, they will occur several days before the rash. The rash itself is in almost all cases visible on the face and from that it spreads to the body and arms and legs. Women need to know that it usually takes three days for the rash to disappear. After the rash has cleared, it is highly likely that a person will develop polyarthritis and polyarthralgia. These occur mostly in adolescent and adult women in a period of 7 days after the rash has cleared. According to the data, up to 70% of all women may develop them.
Vertical transmission and risk of CRS
Not a lot of women know but fetal infection is acquired Hematogenously. However, the rate of transmission is not the same with all women. The rate will depend a lot on the gestational age at which maternal infection occurs. Placenta is the first thing that will get infected by the virus. After that, the virus will reach the fetus through its vascular system. When that happens, the virus will cause cytopathic damage not only to the blood vessels but to the ischemia in developing organs. If the pregnant woman gets exposed to the rubella virus during the first trimester, there are 80% chances of the fetus getting infected as well. The chances are a lot smaller once the woman is in the second trimester. The chances then are 25%. However, once the woman has entered the late second trimester, the chances increase again and range from 35% at a period between 27th and 30th weeks’ gestation up to 100% after the period of 36th weeks’ gestation. According to the experts, the risks of congenital defects are as high as 90% in cases when the maternal infection occurs before the 11th weeks gestation. However, women should be aware that the risk decreases as the weeks’ gestation grows longer. For instance, the risks are 33%at 11-12 weeks, 11% at weeks 12-13 and 24% at weeks 15-16. After the period of 16 weeks, the risk is 0%.
Treatment options of rubella in pregnant women
First of all, women need to know that there is no one treatment of rubella infection during pregnancy and the management must be individualized. Another very important factor in treatment is at which time during gestation the woman was exposed to the virus. The state of immunity of a woman is another factor which is also taken into consideration when treatment options are considered. It is a known fact that it is not an easy task for the doctors to diagnose a pregnant woman with rubella. The main reasons why that is so, are because clinical diagnosis are unreliable due to the fact that a large proportion of cases are subclinical and also because the symptoms which point to rubella infection are quite similar to the symptoms of other diseases. The first thing that needs to be done if a pregnant woman starts showing signs of rubella or some other diseases which is similar to it, gestational age must be determined. In addition to this, the state of the woman’s immune system needs to be determined as well. These things are done as well if the woman has been exposed to the virus in the near past. The treatment of acute rubella infection is supportive and women who are diagnosed with the disease need to know that the prognosis is really good in almost all cases. According to the experts, the best way of treating rubella virus is prevention. Due to that fact, all women who are about to enter their child-bearing years need to get vaccinated.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...