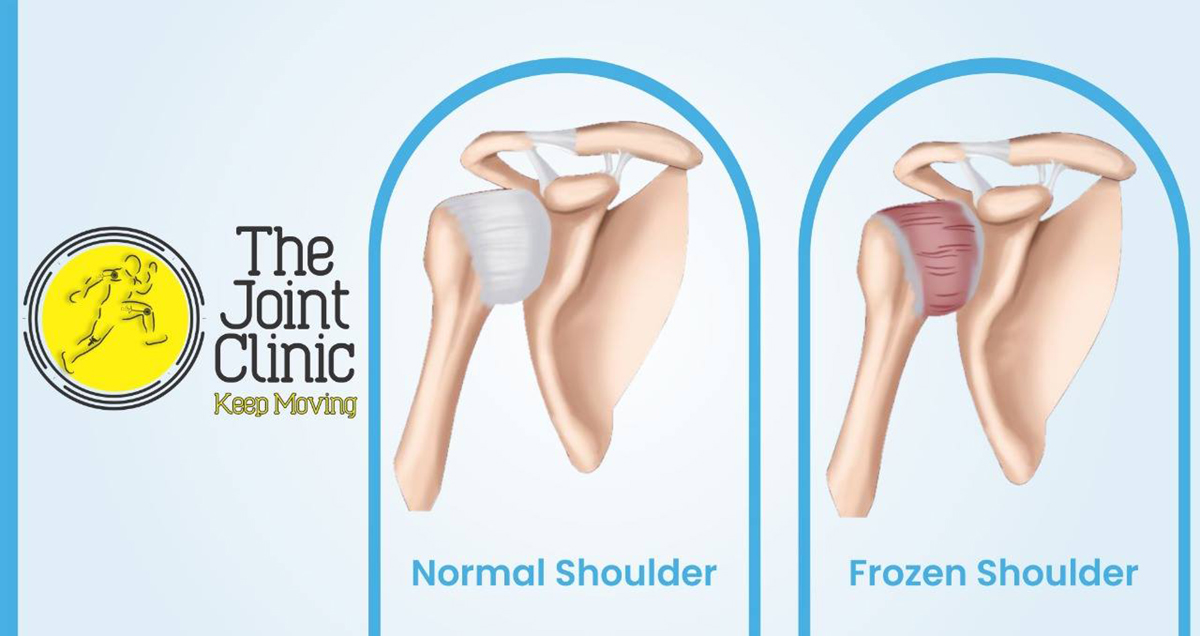
Frozen shoulder is a one of the few medical mysteries. It is quite often diagnosed incorrectly and is the worst of all shoulder problems. The condition is very debilitating and is instantly recognized by severe pain and stiffness. It never has anything to do with any underlying condition and once it gets cured it usually never comes back. Frozen shoulder syndrome is more common in women and is more likely to occur in people who suffer from diabetes or Dupytren’s contracture.
It is not uncommon that it runs in the family, it usually affects older people and it sometimes has a hyper responsive auto-immune component. The symptoms of the frozen shoulder syndrome can last up to 30 months and one experiences four different phases of the syndrome during this period. Pre-freezing is at the beginning and it lasts for a week. The actual freezing can last up to eight months. The frozen phase can be up to sixteen months long. Thawing is the fourth and the last phase and it can last for about a year.
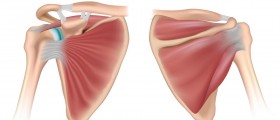
When the lax capsular sack gets sticky it sometimes causes adhesions. The inflammatory state is caused by the interval of the rotator and it usually starts right behind the tendon of the biceps. The inflammation spreads into other soft tissues of the shoulder and caused the shoulder sacks to become swollen. All of this happens because of the interconnection of the shoulder elements and tissues.
The stiffness occurs as a result of the bodily reaction to the muscle inflammation. The body switches off the muscles in a sequence called the capsular pattern. The arm becomes frozen and its movement gets severely restricted. This happens because rotator cuff muscles waste away and become weak.
Up till now there was not any medical approach that could provide a successful treatment for the symptoms of the frozen shoulder syndrome. But now it can be treated with the Niel-Asher technique. This type of technique reduces inflammation and reprograms the switched off muscles. Other conventional methods of treatment include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications for the reduction of pain and swelling but these rarely do improve the condition. Short courses of high doses of intravenous steroids can be helpful in relieving the pain.
Steroids can also be taken orally but they provide mixed results. The method of hydroplasty can be efficient but poses certain risks. Other methods of treatment include hydrodilation, acupuncture, physical therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and manipulation under anesthesia.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...