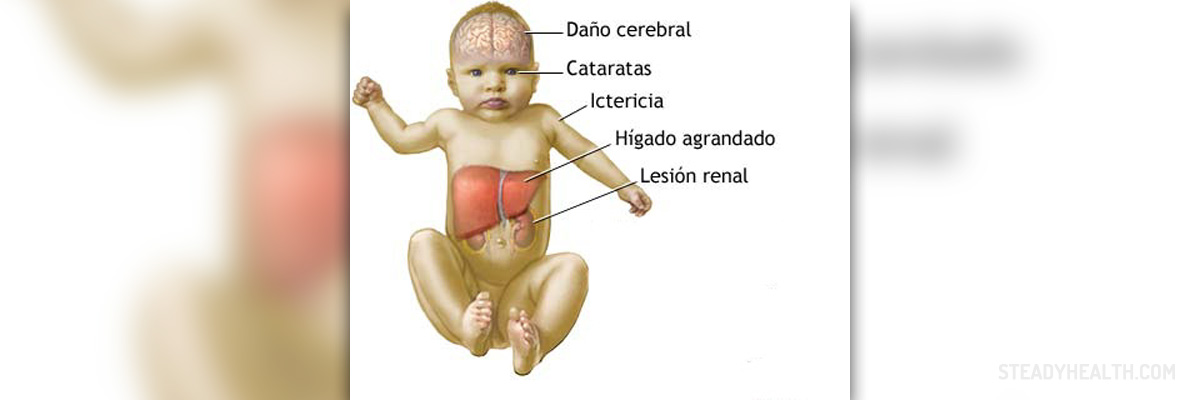
Definition of Galactosemia
Galactosemia is a type of genetic disorder of the metabolic system which is characterized by the lack of an enzyme responsible for degenerating of galactose. Sugar is composed of lactose, which is metabolized into galactose and glucose. When the system is unable to further break down galactose, it builds up and leaves adverse consequences on many internal organs, such as the kidneys and liver, while at the same time causing cataract and developmental problems. Being lactose intolerant entails abdominal pain upon digesting dairy products, while suffering from galactosemia encompasses permanent damage of internal organs if the patient intakes the same type of food. As galactosemia is a genetic disorder, it is passed on from parents to children, in particular through two copies of recessive genes which carry the disorder. The parents usually do not exhibit any symptoms and in most cases are not even aware of the fact that they carry such genes. For this reason, it is highly recommended that parents go through genetic counselling before conceiving. If a child is born with a predisposition for developing galactosemia, he or she should not be breast fed until it is known for sure whether or not the disorder is present. Newborns with galactosemia are usually fed with soy-based formula. In addition, there are various types of long term problems that result from galactosemia and some include cognitive impairment, physical disability, eye problems and ovarian failure in girls.
Treatment for Galactosemia
At this time, no medical treatment is available for galactosemia, except a very strict doctor recommended diet. As mentioned previously, eating foods that contain lactose and galactose can result in severe organ damage so those should be left out of the diet, which primarily means no dairy products. Various type of meat should also be avoided as those contain galactose. Since the onset of galactosemia is right at birth, it’s the responsibility of the parents or caregivers to ensure the child is fed properly. There should be medical professionals involved, such as paediatricians and nutritionists, to advise the parents and keep them informed about the constant changes that surround the treatment of galactosemia. It is also crucial that the child is raised and treated like any other, with fairness, consistency and positive examples. A child with such a complicated, continous disorder needs to be taught discipline, as one day he or she will be the one responsible for their own well being. Teaching a child which foods are acceptable and which are not should be the same kind of activity as teaching colors, animals, or other types of approved behavior, such as saying ‘thank you’ and ‘please’. On average, it is expected that a child in kindergarten knows that milk products are not acceptable. By the onset reaches the puberty it should know all the foods that are not permitted.
Help Your Child
In order for the parents and caregivers to be able to help their child live with galactosemia, they have to be informed about all of the aspects of the disease, especially the types of food that should not be consumed. For instance, if a label of a food product reads curds, whey, sodium caseinate, casein, or non-fat dry milk, such substances all contain lactose or galactose and should not be eaten. Food products which contain those same elements are canned soups, creams, cakes, candy and the like. On the other hand, if a label of a food product reads lactate, kosher, or ‘Parve’, it is safe to use. Keep in mind that some foods do not contain labels and for safety reason should be refrained from. Further, during childhood and later in adulthood, a good substitute for milk includes soybean protein isolate formulas. On the other hand, milk substitutes which include whole soybeans, soy milk, soy protein and the like should later in life be avoided, while milk alternatives which are based on rice are permitted. In general, pastas and rice are allowed, but individuals should be careful with cereal. In the case of fruits and vegetables, it is hard to say which are acceptable and which are not. It is best that the patient consults with a long term medical care provider as every case is different. When it comes to meat, chicken, beef, pork and fish, all are acceptable, while the insides such as liver and brain are not. It is not necessary to exclude sweets from the diet and desserts such as gelatine, certain types of pudding, hard candy that does not contain chocolate and various kinds of artificial sweeteners are tolerable. Further, dining in a restaurant can be challenging but not impossible as there are many who will take special requests and make their customers happy. It is advisable to find places that suit the dietary needs and to stick with them. In some cases, a doctor may also recommend dietary supplements of Vitamin D and calcium.

















Your thoughts on this
Loading...